Welcome all anatomy students! It has been a while since I posted a lesson because, frankly, I have been dealing with my own malady – a shattered left ankle! Six months out and beginning to feel and function better. 🥳
Outlander fans recall that in episode Episode 702, “The Happiest Place on Earth,” Brianna gives birth to her second child, Amanda Hope Claire MacKenzie-Fraser. Dr. Claire is there to reassure Brianna and ease the process. The wee one is adored by all and affectionately nicknamed, Mandy. Fraser’s Ridge is the happiest place on earth and all is well! 🥰

Young Mandy is quickly introduced to the Ridge’s denizens as Granda’ Jamie takes her on a wee stroll to meet a new foal at the stable. Do you see it, Mandy? It is a cutie-beauty like you! 😍

Mandy’s doting Granny takes her on a guided tour of Claire’s fav room – the surgery! Mayhap she will follow in Granny’s footsteps? 👩🏻⚕️
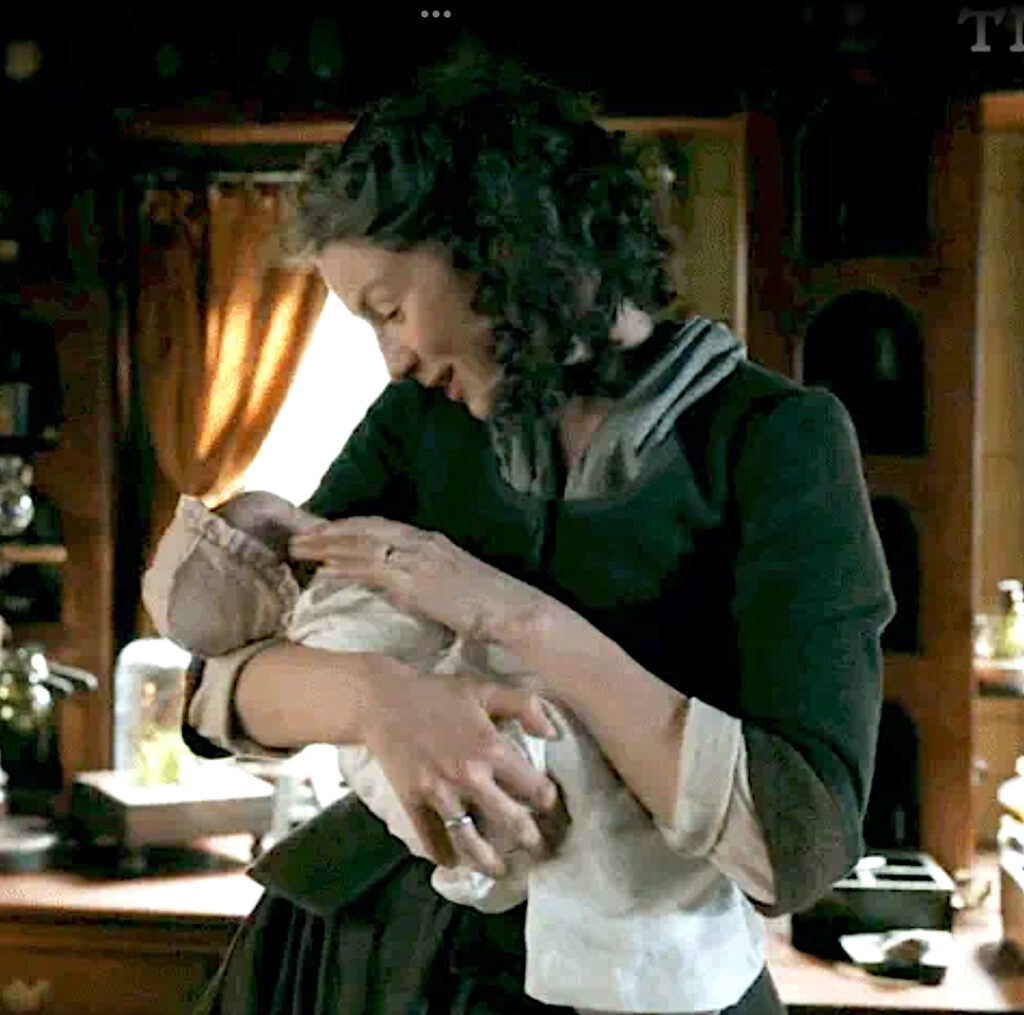

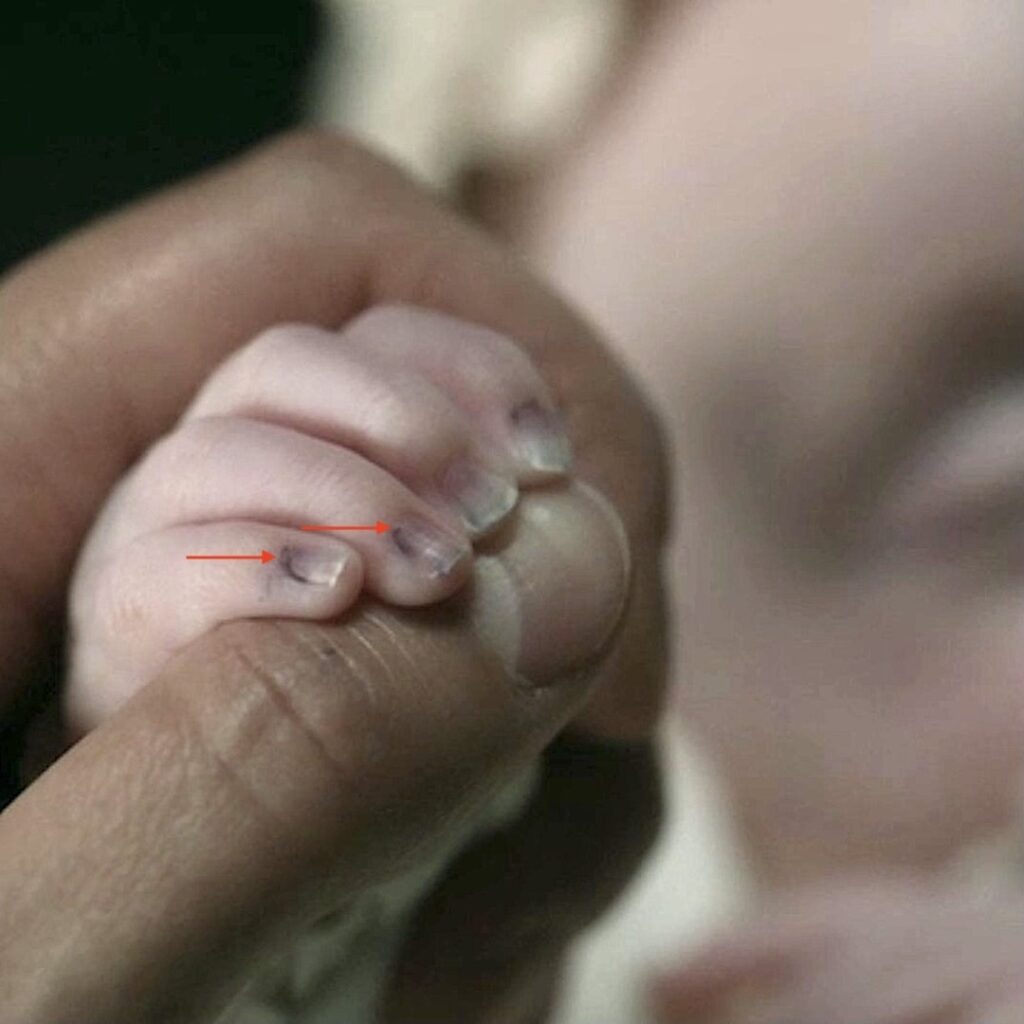
Claire coos to Mandy, admiring the beautiful, wee lass. Then…. she sees Mandy’s fingernails. A closer look and a startled Claire exclaims: “Bloody hell!” (Couldn’t have said it better myself)
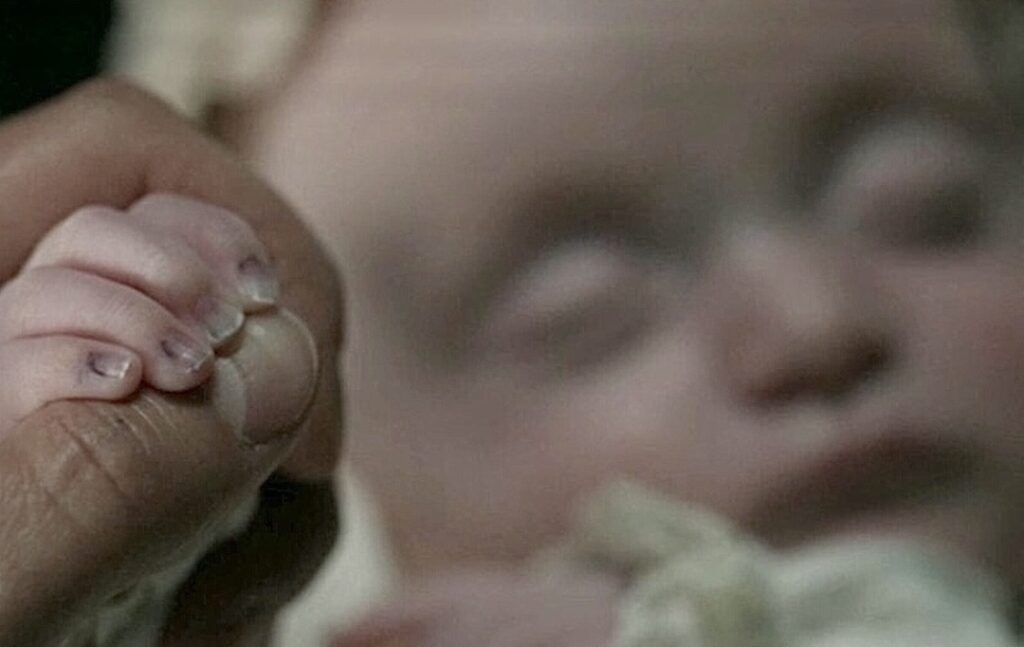

Ever observant Claire spies a bluish tinge at the base of Mandy’s wee fingernails (below, red arrows)!
Fun Fact: This is not hyperbole. Fingernails and toenails give clues to at least a dozen possible medical conditions that require evaluation and followup. And, Mandy is no exception.
A quote from Diana’s 6th big book, “A Breath of Snow and Ashes,” documents the moment Claire observes Mandy’s nail beds: ”
“The minute nails were faintly tinged with blue.”
Bree senses Claire’s concern and asks what is wrong. She kens that look on her mother’s face. After Claire explains, Bree reports her own maternal observations: Mandy does not nurse well nor is she gaining weight like Jem. What is wrong? 😯
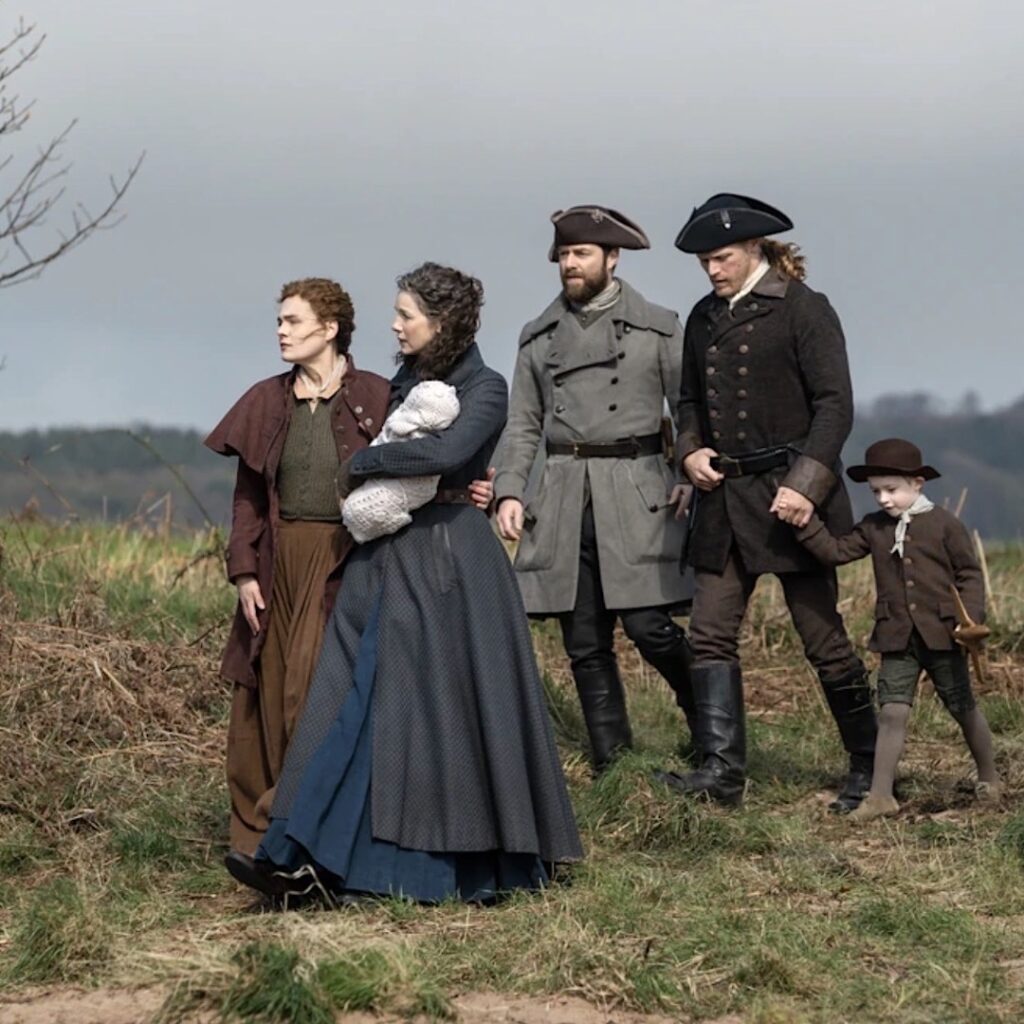
Claire determines that the wee lass has a heart defect requiring more advanced care than Claire is able to provide in the 1700s. She is clear that Mandy’s Malady is life-threatening and she likely will not survive for long without corrective cardiac surgery. Brianna and Roger decide to return with their children to the 20th century to obtain the necessary care to save Mandy’s life.
Arrangements are made for the MacKenzie family to travel through time at the standing stones on Ocracoke Island. Everyone agrees this is the best course of action, but this time and place is no longer the “happiest place on earth!” Will they ever see Fraser’s Ridge and one another again? 🤷🏻♀️

Time to start our lesson….What leads Claire to her startling diagnosis? The following are symptoms and clues that Doctor Claire considered:
-
- Lethargy and weakness
- Fast or labored breathing
- Tachycardia (a heart rate exceeding the normal resting rate)
- Cyanosis (blue-ish skin color due to a lack of oxygen), primarily seen in lower extremities
- Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
- Poor feeding
- Failure to thrive
- Distinctive murmur
Another pithy quote from “A Breath of Snow and Ashes:”
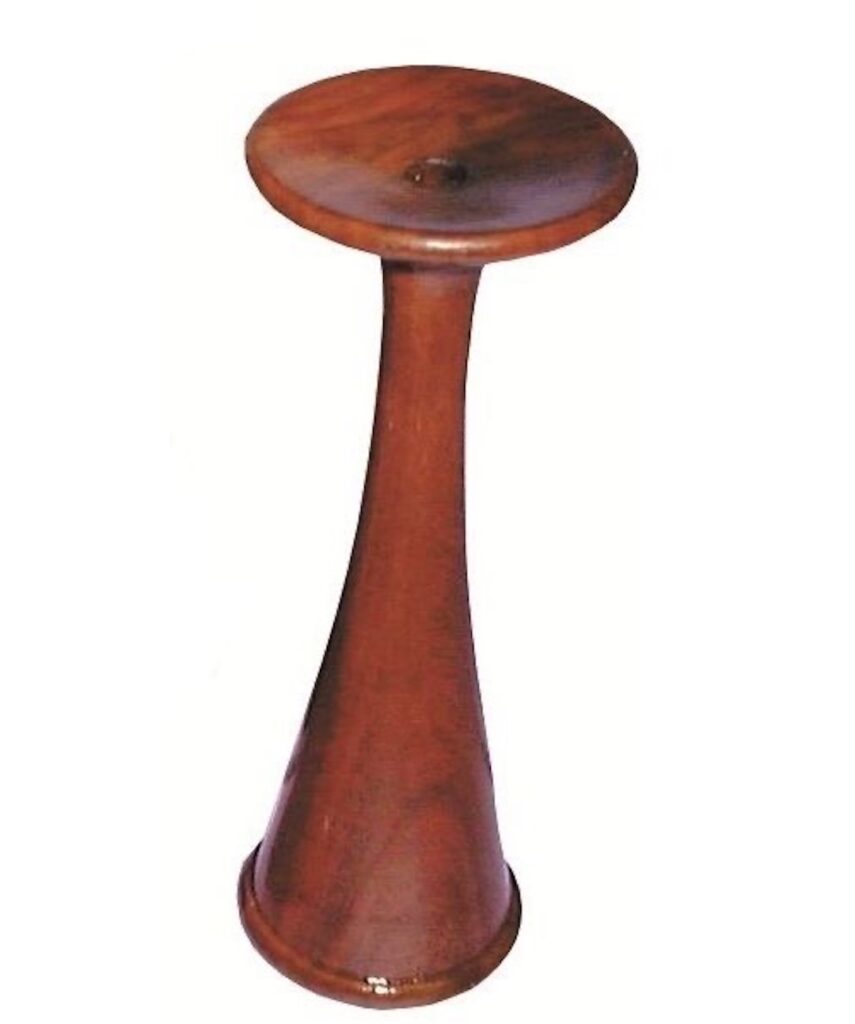
I moved my stethoscope over the tiny chest, ear pressed to it, listening intently. It was my best stethoscope, a model from the nineteenth century called a Pinard—a bell with a flattened disc at one end, to which I pressed my ear. I had one carved of wood; this one was made of pewter; Brianna had sand-cast it for me.
The following image is a wooden Pinard stethoscope, currently for sale on the Internet for about $180 (there are much less expensive versions)! 💰
Claire placed her ear against the cup shaped disc at the top; the bottom of the tube was placed on Mandy’s chest. The stethoscope amplifies the sounds of blood rushing through the heart and striking its valves.
What did Claire listen for? she was listening for a distinctive murmur: a soft, continuous shushing sound, particularly audible near the base of the neck. It is usually the first diagnostic sign of a problem with a fetal heart vessel.

Although Mandy exhibits only some of the above symptoms, Claire diagnoses Mandy’s condition as a Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA).
But, before we can understand PDA, let’s look at normal heart anatomy.
Heart Anatomy: To better understand Mandy’s Malady, let’s consider the normal anatomy of the heart and its great vessels. Now, I kid you not, the heart is a very complex organ, both anatomically (structure) and physiologically (function). We will only cover the basics. Understand that there are many more anatomical details that are beyond the scope of this lesson. But, we fearless folk press onward!
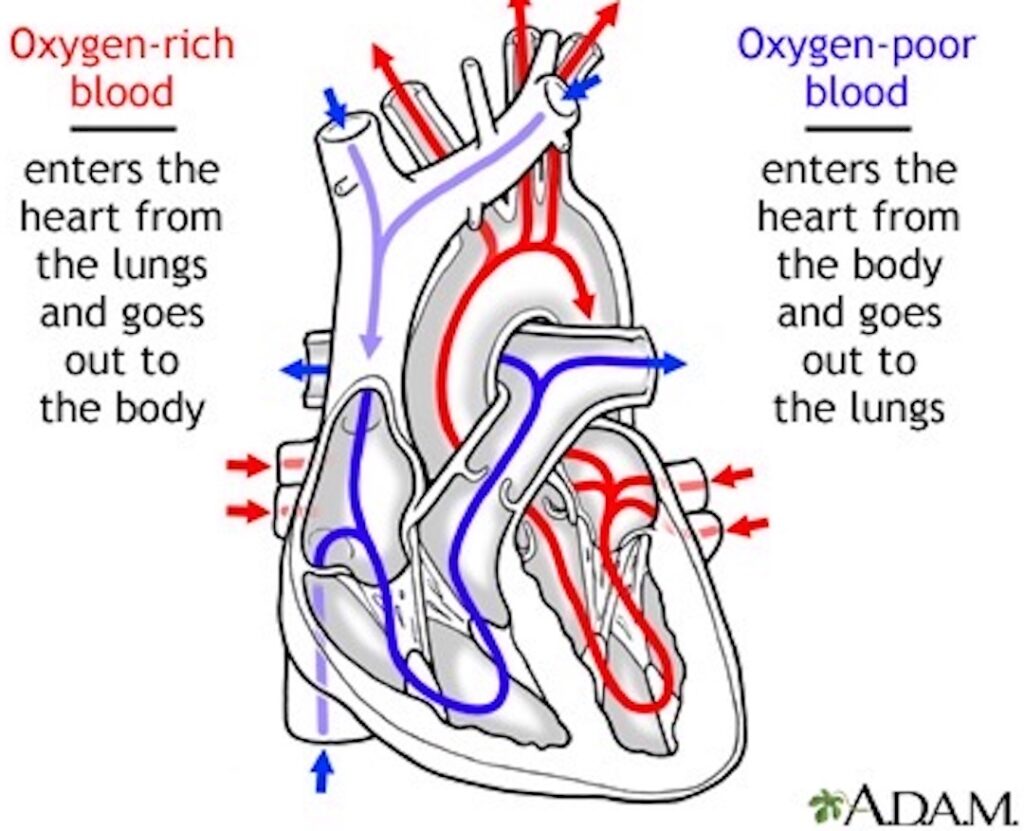
Chambers: The human heart has four chambers (next image). Right atrium and left atrium are thin-walled filling chambers. Right ventricle and left ventricle are thick-walled pumping chambers . The walls are composed of cardiac muscle, a specialized tissue found in the heart. (psst….don’t forget, the patient’s left is your right, and vice versa) 🤓
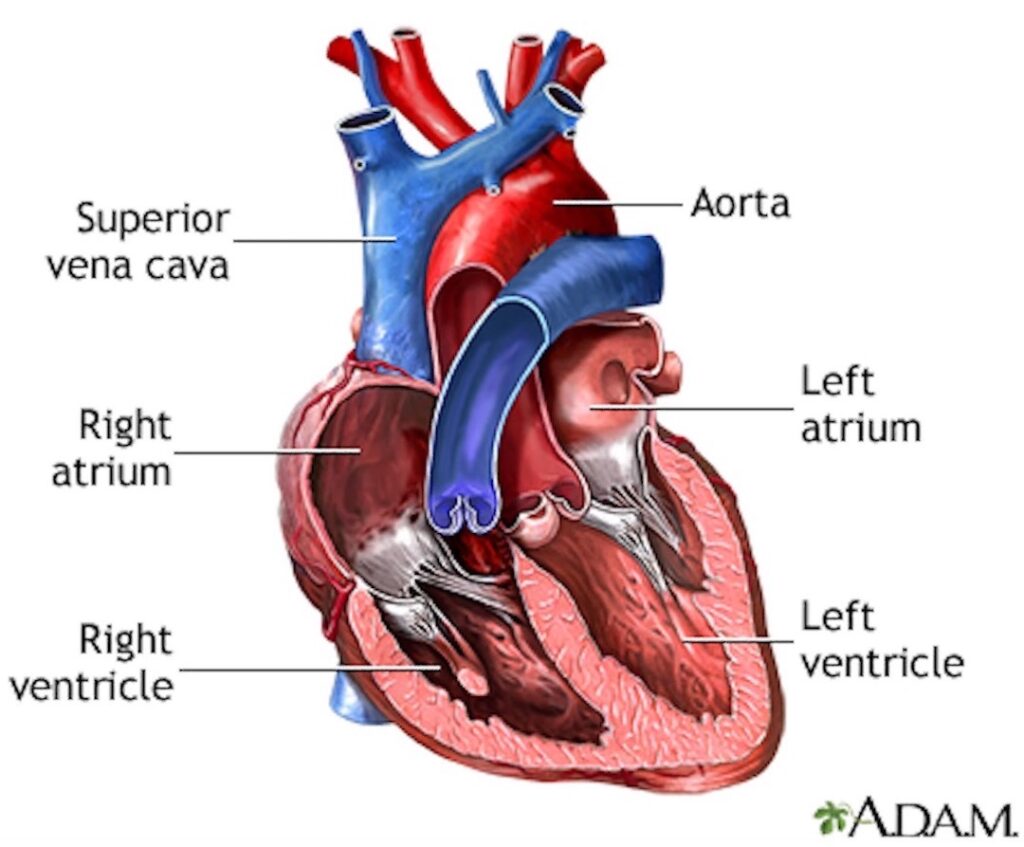
Vessels: The heart has eight (!!!) vessels carrying blood to and from its chambers. These are (next image):
-
- Superior vena cava – delivers blood from upper body into right atrium
- Inferior vena cava – delivers blood from lower body into right atrium
- Pulmonary artery – deliver blood from right ventricle to lungs
- Four pulmonary veins – deliver blood from lungs to left atrium
- Aorta – delivers blood from left ventricle to body
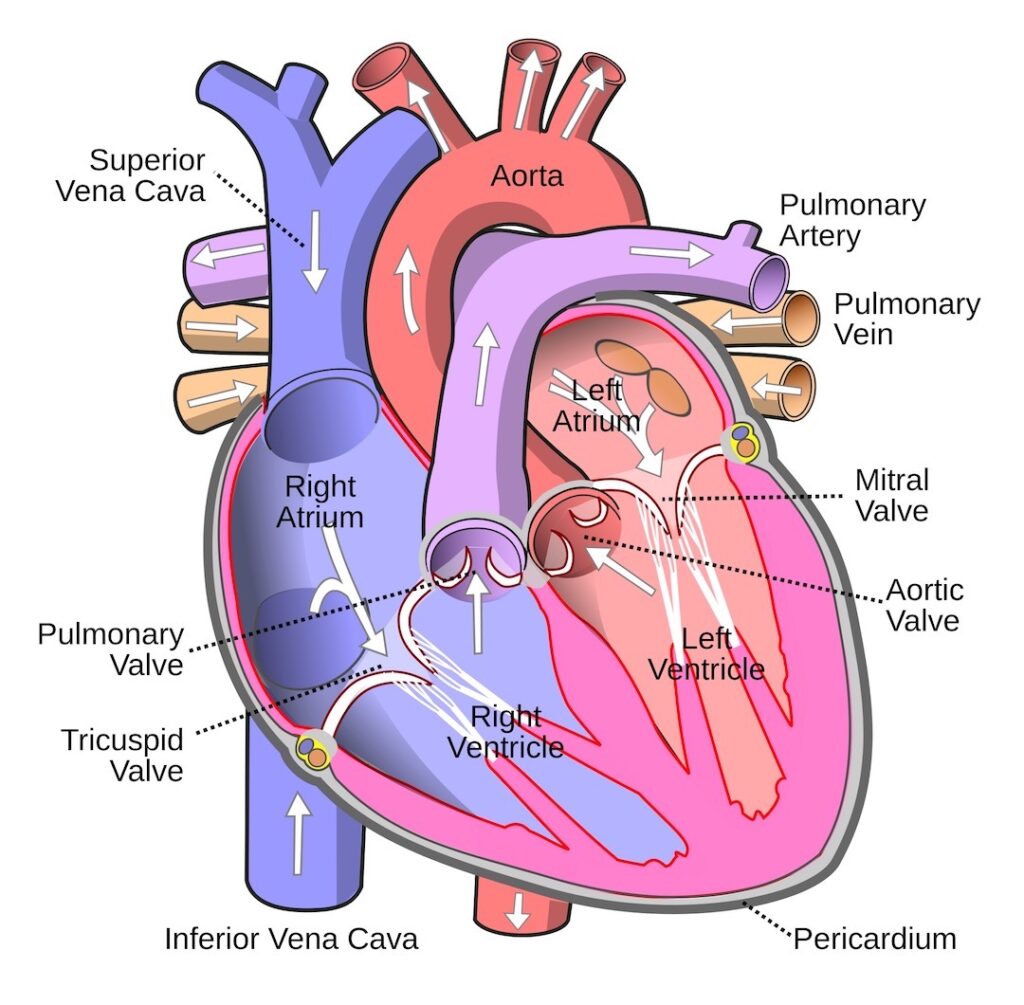
Blood Flow: Next, let’s review the pattern of blood flow through the heart. As you read the details, check with the image below to verify the flow.
-
- Deoxygenated blood (low oxygen – O2; high carbon dioxide -CO2) from superior vena cava and inferior vena cava pours into right atrium and then into right ventricle.
- Right ventricle contracts and ejects blood into the pulmonary artery which branches to supply left and right lungs.
- Blood releases carbon dioxide (CO2) in the lungs which is exhaled and picks up O2 from inhaled air.
- Oxygenated blood (O2-rich) is carried to left atrium via four pulmonary veins.
- Blood pours into the left ventricle which contracts and ejects O2-rich blood into the aorta.
- Branches of aorta carry blood to all other regions of the body (except lungs).
OK, students, hang in there! With normal anatomy under our belt, let’s look at the fetal circulation.
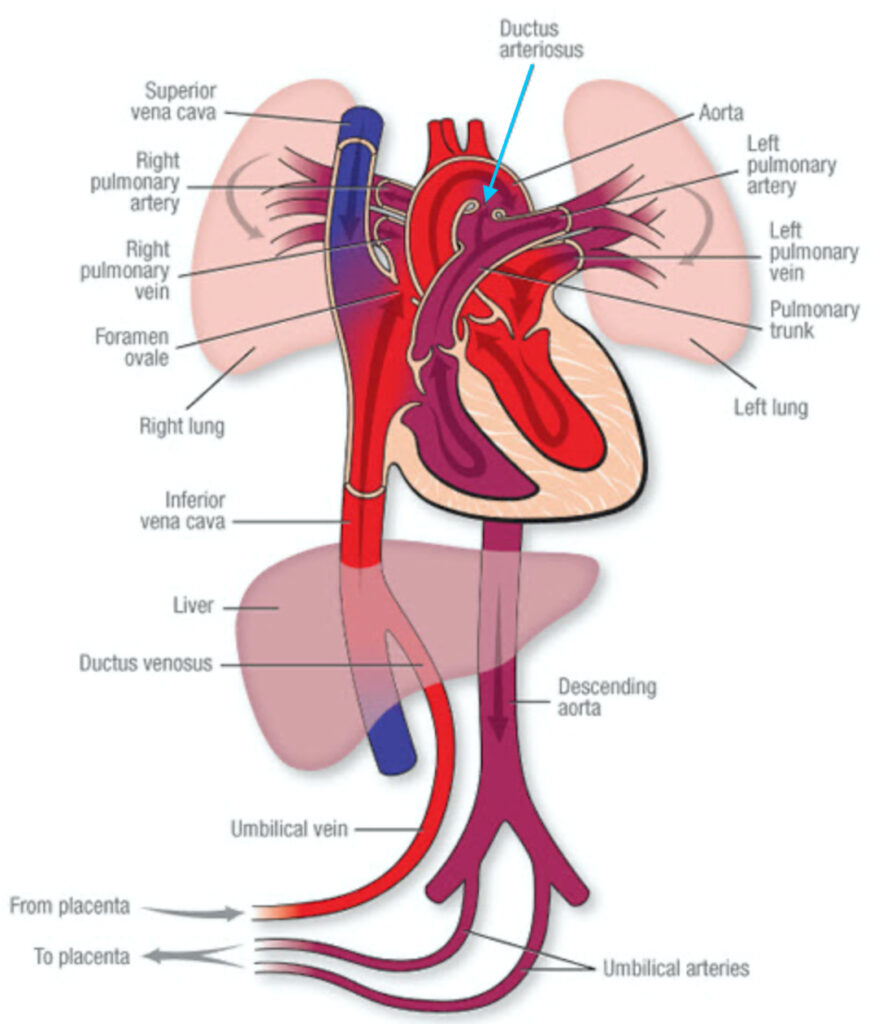
Fetal Circulation: Blood circulation in the fetus is different because the placenta provides the functions of lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys. Thus, a normal blood supply to these maturing organs is not required.
Ductus Arteriosus: The fetal heart has a vascular bridge between pulmonary artery and aorta that shunts blood exiting the right ventricle into the aorta and bypasses the lungs. This vascular bridge is the muscular ductus arteriosus (aqua arrow – below image). Again, because lungs do not process gasses during intrauterine life, most blood is shunted away from them.
The ductus arteriorsus is patent (open) throughout fetal life and normally closes within 24 hours after birth as blood flow to the lungs is established. Within 2-3 weeks, it turns into a fibrous band, the ligamentum arteriosum.
All of this is highly regulated by various chemical and physiological substances including oxygen levels.
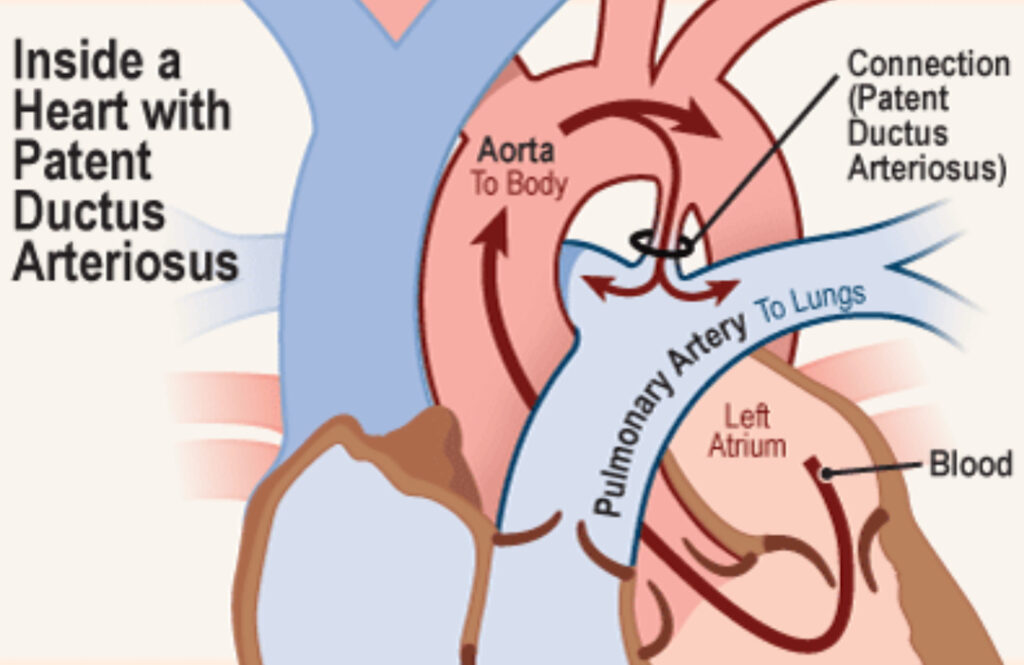
Patent Ductus Arteriosus: If the ductus arteriosus does not close soon after birth but remains patent (open), it is diagnosed as PDA, a congenital heart lesion. PDAs are most common in premature babies but can also occur with full term infants.
Nowdays, if a ductus arteriosus does not spontaneously close after 8 weeks post-birth, it usually is treated with medications, plugged, or surgically closed. Small PDAs may not be a cause for concern and are often not treated.
Adding a bit of perspective – PDA is not new. It was known as early as 129 A.D. to Galen, a Greek anatomist and physician, although he didn’t understand its significance. It wasn’t until 1938, almost two millennia later, that Dr. Robert E. Gross of Harvard Medical School and Children’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, perform the first successful ligation (closure) of a PDA. This was also the first congenital heart lesion to be successful corrected, surgically.
Now, let’s return to Mandy’s Malady. This was her problem. Mandy’s ductus arteriosus did not close after birth and she exhibited some of the concerning symptoms outlined above. Blood from her aorta flooded her lungs subjecting fragile lung tissues to excessive blood pressure (hypertension). Allowed to go unchecked, the fragile lungs will be permanently damaged and she eventually will experience right-sided heart failure.
Diana explains all of this with her usual magical writing skills in this excerpt from “A Breath of Snow and Ashes:”
The ductus arteriosus is a small blood vessel that in the fetus joins the aorta to the pulmonary artery. Babies have lungs, of course, but prior to birth don’t use them; all their oxygen comes from the placenta, via the umbilical cord. Ergo, no need for blood to be circulated to the lungs, save to nourish the developing tissue—and so the ductus arteriosus bypasses the pulmonary circulation.
At birth, though, the baby takes its first breath, and oxygen sensors in this small vessel cause it to contract—and close permanently. With the ductus arteriosus closed, blood heads out from the heart to the lungs, picks up oxygen, and comes back to be pumped out to the rest of the body. A neat and elegant system—save that it doesn’t always work properly.
The ductus arteriosus doesn’t always close. If it doesn’t, blood still does go to the lungs, of course—but the bypass is still there. Too much blood goes to the lungs, in some cases, and floods them. The lungs swell, become congested, and with diverted blood flow to the body, there are problems with oxygenation—which can become acute.
Lastly, this is a brief video about PDA which you might find useful. It is easy to understand and accurate: https://youtu.be/7DKaCqubuSg. 🤓
Fast forward! It is clear that the MacKenzies arrived safely in the 20th Century and Mandy received the medical intervention needed for her PDA repair. When we meet her next at Lallybroch, she is a healthy, happy, and feisty wee lass, played by Rosa Morris. 🤗

As William Shakespeare once wrote, “All’s Well That Ends Well!”
(Well, it would end better if they were all together, but we shall see) 🤞🏻
The deeply grateful,
Outlander Anatomist
Follow me on:
-
- Twitter: @OutLandAnatomy
- Facebook: OutlandishAnatomyLessons
- Instagram: @outlanderanatomy
- Tumblr: @outlanderanatomy
- Youtube: Outlander Anatomy
Photo creds: Sony/Starz; www.commons.wikimedia.org; www.heart.org; www.kidshealth.com; www.medicalsuppliesgh.com; www.medlineplus.gov; www.outlander.fandom.com; www.theoutlandermuse.com; www.twitter.com (now X)