Hey, all.
Hope you had a grand couple of weeks awaiting part two of Outlander Trauma-Drama… Here it is. Yay! 🤗
Our last Anatomy Lesson, Outlander Trauma-Drama, Part 1, showed the system pathologists use to classify trauma. In that lesson, we covered different types of mechanical trauma including contusion, abrasion, laceration, incision, avulsion, projectile injury, and puncture wounds.
Remember? Yasss! 😊
-
- Mechanical trauma
- Contusion
- Abrasion
- Laceration
- Incision
- Avulsion
- Projectile injuries
- Puncture wounds
- Thermal Injury
- Radiation Injury
- Personal Exposure (tobacco and alcohol)
- Therapeutic Drugs
- Air Pollution
- Industrial Exposures
- Agricultural Hazards
- Natural Toxins
- Oxygen Deprivation
- Infectious Agents
- Immunological Diseases
- Genetic Derangements
- Nutritional Diseases
- Mechanical trauma
Today’s lesson continues with the trauma-drama theme ‘cos there are still loads of Outlander owies to uncover and discover!
Again, examples from Diana’s big books and the Starz Outlander series will serve as anatomical models for the injuries. 👍🏻
Today’s lesson will cover thermal injury and alcohol abuse. So, let’s get started!
There are six types of Thermal Injury:
-
- Thermal burns
- Hyperthermia
- Chilblains
- Hypothermia
- Frostbite
- Electrical injury
Here we go!
Thermal Burns: Thermal burns are caused by harmful exposure to heat, electricity, chemicals, or radiation.
Thermal burns are usually classified as first, second, or third degree burns. Occasionally, we hear of fourth degree burns, but do you ken there are also fifth and sixth degrees? Indeed there are! 🤓
Some students may have read Anatomy Lesson #5 and Anatomy Lesson #6 wherein we learned that skin is composed of epidermis (surface layer of skin cells) and dermis (underlying connective tissue). Thus, another useful way of grading thermal burns is to describe their relative depths.
Partial-thickness Burn: This type damages the epidermis or both the epidermis and outer dermis; it includes first and second degree burns. Such burns are red and may blister and are very painful. Most partial-thickness burns heal without scarring because hair follicle cells regenerate to cover the damaged surface. Even here, if a partial-thickness burn is too large, a skin graft may be required.
Full-thickness Burns: Full-thickness burns extend through both epidermis and dermis and into underlying tissues. Such wounds are typically aesthetic (painless) because nerve endings are destroyed, although the rim of such a burn is usually painful. Full-thickness burns include third, fourth, fifth and sixth degree burns which may pass into muscle and bone. Fifth and Sixth degree burns are typically fatal.
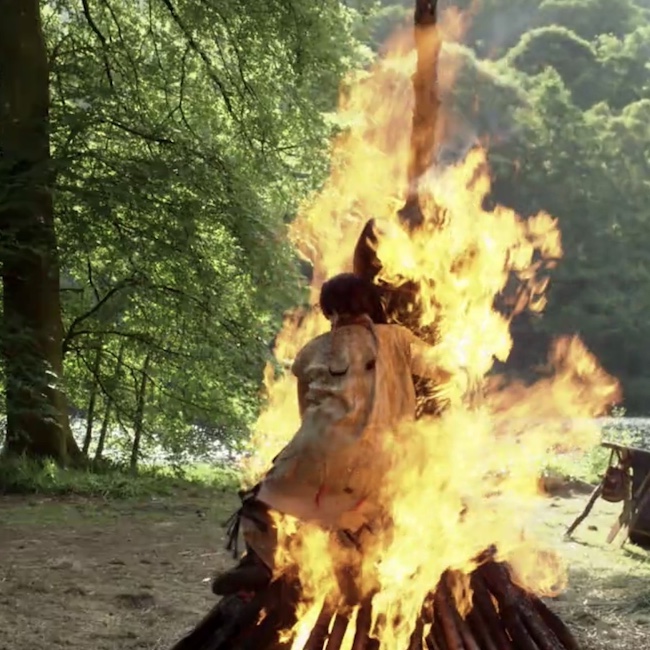
We can imagine fifth and sixth degree burns suffered by poor Father Alexandre and Johiehon, his love interest in Outlander episode 412, Man of Worth.
Diana’s fourth big book, Drums of Autumn details the sad and horrific conflagration as the lovers burned to ash.
When the Indians had nearly finished with the priest, they untied him from the stake and fastened his hands instead to a long pole, held above his head, from which to suspend him in the flames….
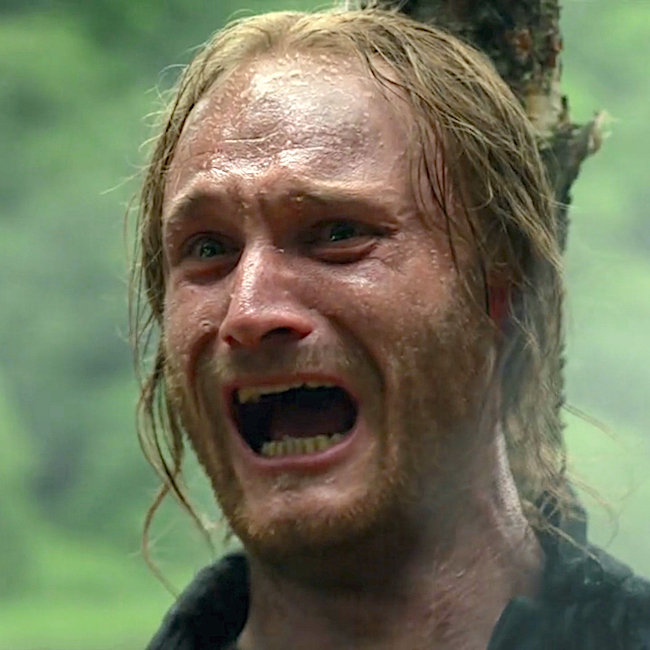

… It was then that he had seen the Indian girl standing on Claire’s other side, with a cradleboard in her arms. … “She didna look to left or right, but walked straight into the fire.” … The flames had embraced the girl in moments.
… “Her clothes caught, and then her hair. By the time she reached him, she was burning like a torch.” Still, he had seen the dark silhouette of her arms, raised to embrace the empty body of the priest. Within moments, it was no longer possible to distinguish man or woman; there was only the one figure, black amid the towering flames.
…The smell of burnt things hung in the air. We passed close by the pit and I couldn’t help seeing from the corner of my eye the heap of charred fragments, shattered ends frosted white with ash.

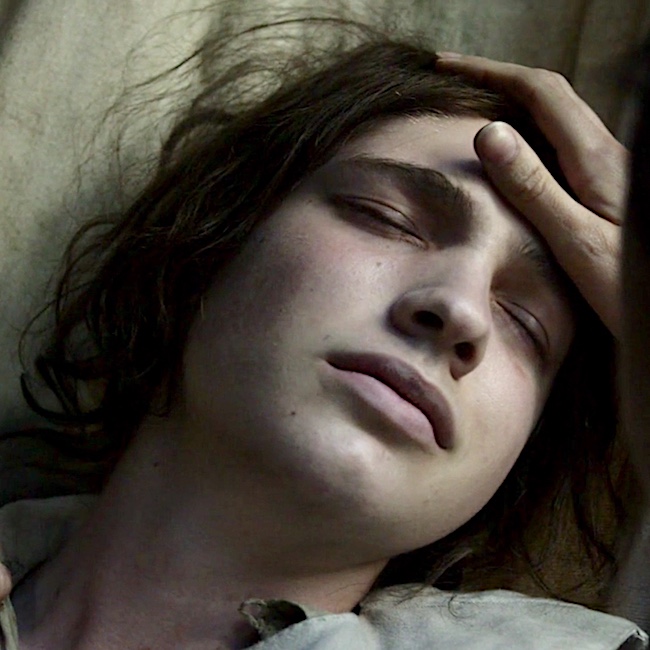
Hyperthermia: Hyperthermia occurs if body temperature rises significantly above normal (>104 °F / 40 °C ). Many challenges, including infections, cause excessive body temperature.
Typhoid fever, a.k.a. enteric fever, is caused by food and water contaminated with salmonella bacteria. Symptoms include:
-
- High fever
- Headache
- Stomach pain
- Constipation or diarrhea
A great example of hyperthermia appears in Outlander episode 310, Heaven and Earth. You remember Claire’s splendid wee aide, Elias, who falls ill with typhoid? Claire is comforts him as he bravely succumbs to fever and dehydration. 😭

Cold temperatures 🥶 also cause thermal injury because the human body is poorly equipped to regulate and prevent heat loss; this is especially true of children and the elderly. Normally, fat deposits, heart, blood vessels, brain, skin, and muscles help combat cold. These organs provide insulation, induce shivering, re-direct blood flow from skin to vital organs, and reduce energy consumption.
However, exposure to cold temperatures over long periods of time overcomes our coping mechanisms and produces a range of thermal cold injuries such as chilblains, hypothermia, and frostbite.
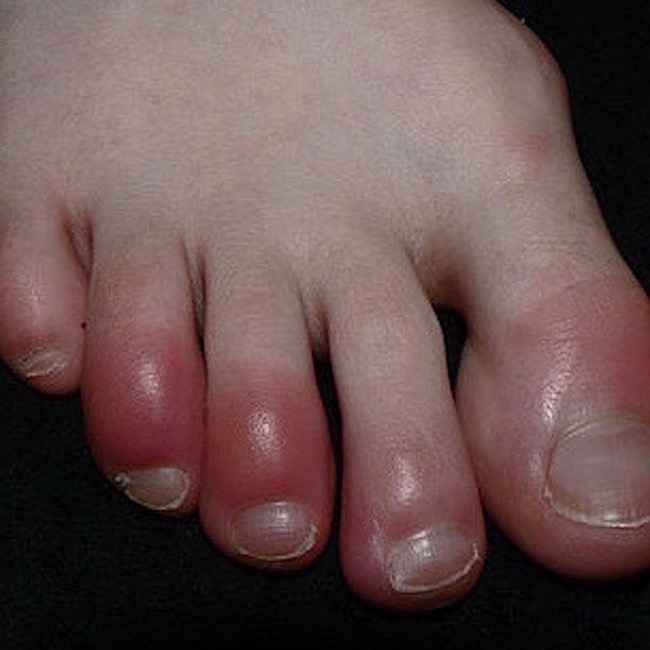
Chilblains: Chilblains is a 16th century term for skin trauma due to repeated expose to cold, but not freezing, air. Digits are most commonly affected. The skin becomes red, swollen ,and itchy (next image), but usually heals without permanent damage.
Outlander TV episodes do not feature chilblains. But have no fear, our amazingly witty and resourceful Diana writes about it in her second book, Dragonfly in Amber, wherein Claire treats imprisoned men with chilblains.
She’s a wonder! Which “she” do I mean? Take your pick – either woman works!
I talked my way into the cells of the prison, and spent some time in treating the prisoners’ ailments, ranging from scurvy and the more generalized malnutrition common in winter, to chafing sores, chilblains, arthritis, and a variety of respiratory ailments.
Ouch, that looks a wee bit uncomfortable!
Hypothermia: Hypothermia occurs when the body’s core temperature drops below 95°F / 35°C as a result of extended cold exposure. Symptoms include low core temperature, vigorous shivering, confusion, sleepiness, slurred speech, shallow breathing, weak pulse, low blood pressure, changes in behavior, and slowed reactions.
Put simply, the victim of hypothermia experiences the “umbles” meaning grumbles, mumbles, stumbles and fumbles because cold affects muscle and nerve response.
If the core temperature drops to 90º F / 32.2º C, then bradycardia (slow heart rate) and atrial fibrillation (fast and irregular contraction of the heart’s two upper chambers) may ensue.
The teenager, bad-lass Laoghaire, wasn’t suffering from hypothermia when she exposed her “ladies” to Jamie in Outlander episode 109, The Reckoning, but she was well on her way!
Take a keek at that goose flesh! 😉

Frostbite: Frostbite is cold injury in which the body’s surface is exposed to freezing temperatures; it affects mostly feet, hands, noses, cheeks, and ears. And, as Prince Harry points out in his tell-all book, “Spare,” the todger must be protected from frostbite. This makes sense since it is also an appendage. 😉
Frostbite occurs in three stages:
-
- Frostnip: Frostnip is a mild form of frostbite. Continued cold exposure leads to numbness in the affected area. As the skin warms, the sufferer feels pain and tingling but no permanent skin damage.
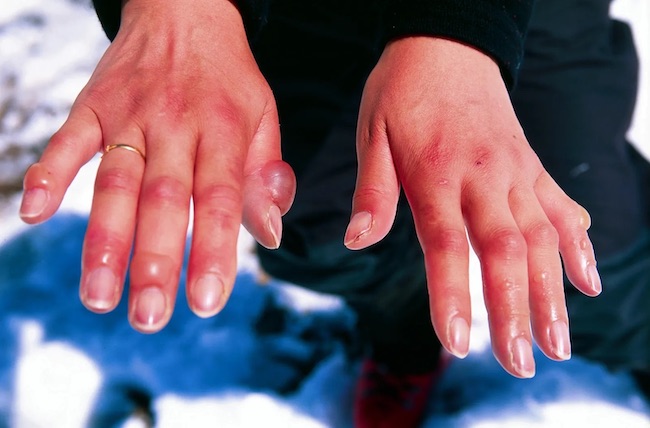
- Superficial Frostbite: Superficial frostbite causes slight changes in skin color. The skin may begin to feel warm — a sign of serious skin damage. Rewarming at this stage causes the skin to appear mottled. The victim may notice stinging, burning and swelling. Fluid-filled blisters may appear over the next 12 to 36 hours (next image).
- Deep Frostbite. As frostbite progresses, it affects all layers of the skin and underlying tissues. The skin turns white or blue-gray; all sensation of cold, pain, or discomfort is lost in the affected area. Joints or muscles may stop working. Large blisters form 24 to 48 hours after rewarming. The tissue turns black and hardens as it dies. Amputation is usually warranted.
Claire teasingly relates how she and Jamie avoid getting frostbite in this steamy tidbit from Drums of Autumn.
His mouth was warm and soft, and whether he approved of what he was doing or not, he did it awfully well.
…“Ooooh,” I said, and shuddered ecstatically as his teeth sank delicately into my earlobe.
….“Oh, well, if it’s like that,” he said in resignation, and taking my hand, pressed it firmly between his thighs.
..“Gracious,” I said. “And here I thought the cold …”
…“It’ll be warm enough soon,” he assured me. “Get them off, aye?”
…It was rather awkward, given the cramped quarters, the difficulty of staying covered in order not to suffer frostbite in any exposed portions, and the fact that Jamie was able to lend only the most basic assistance, but we managed quite satisfactorily nonetheless. 😅

Electrical Injury: What is this? Electrical injury is damage to the skin or internal organs after a person comes into direct contact with a high-voltage source. An electric shock can be life-threatening.
Good advice: Get emergency help if the source of the injury is a high-voltage wire or lightning. Even those with minor injuries or no symptoms should be checked by a physician for internal injuries because these may not be evident to the non-professional.
In the US, there are approximately 1000 deaths per year, as a result of electrical injuries. Of these, approximately 400 are high-voltage electrical injuries and lightning causes 50 to 300. There are also at least 30,000 shock incidents per year that are non-fatal.
If you think these stats are grim, consider the UK: Faulty electrical equipment and sockets cause approximately 70 deaths and 350,000 injuries in UK homes every year (RHA, 2022). Such figures show how important it is to follow electrical safety guidelines.
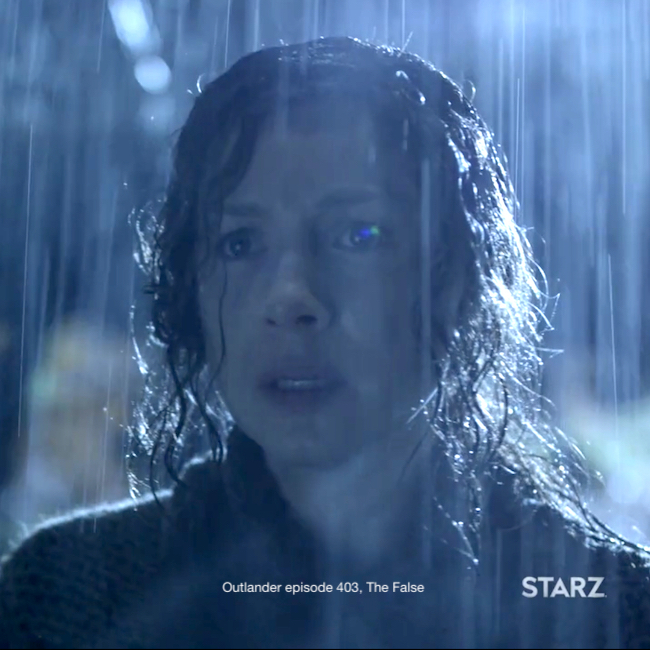
Outlander book and TV don’t really contain much about electrical injury. the closest I can come is Claire’s eerie encounter with Otter-Tooth’s ghost in Outlander episode 403, The False Bride. Here, she experiences the aftermath of a lightning strike.
Diana describes the scene in vivid detail. Again, from Drums of Autumn:
Sheet lightning shimmered far away, across the mountains. Then more bolts, sizzling across the sky, each succeeded by a louder roll of thunder. The hailstorm passed, and the rain resumed, pelting down as hard as ever. The valley below disappeared in cloud and mist, but the lightning lit the stark mountain ridges like bones on an X ray.
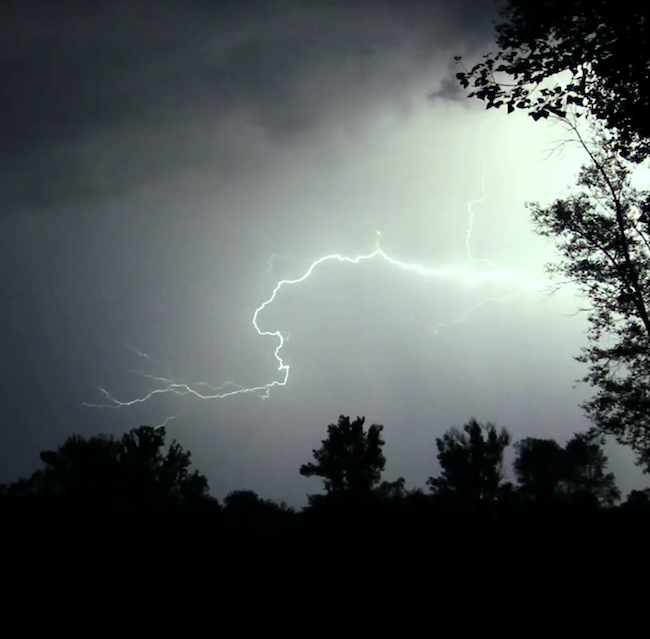

I woke all the way to the smell of burning, and sat bolt upright. The rain had stopped; it was the silence that wakened me, I thought. The smell of smoke was still strong in my nostrils…
…The ground rose in front of me to a small ridge. At the top of this stood a large balsam poplar tree, the source of the smoke. The tree had been struck by lightning; half of it still bore green leaves, the canopy bushy against the pale sky. The other half was blackened and charred all down one side of the massive trunk. Wisps of white smoke rose from it like ghosts escaping an enchanter’s bondage, and red lines of fire showed fleetingly, glowing beneath the blackened shell.
Echoes of the shock of impact wavered through my flesh, and I tried frantically to fit myself back into my body. Then I drew breath, a painful gasp, and found myself shaking, the shock turning to the first intimations of damage. I lay still, eyes closed, concentrating on breathing, conducting an inventory.
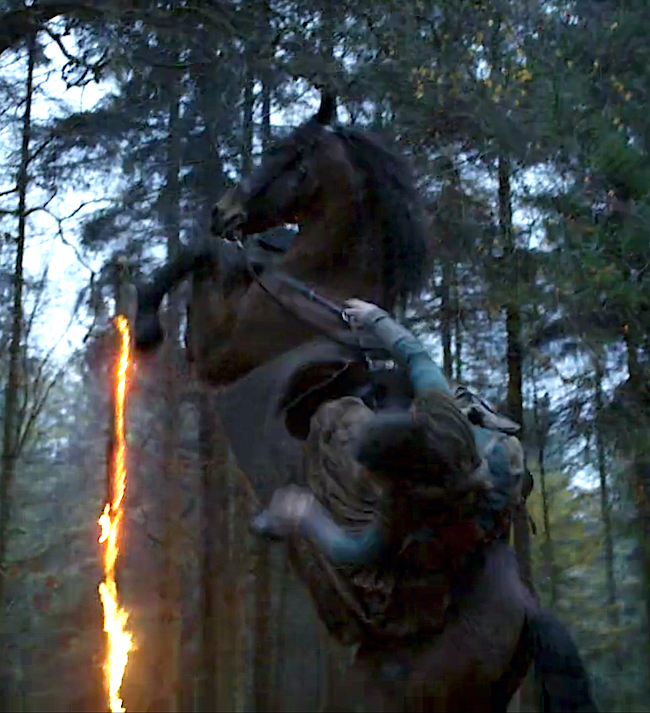

…The rain was still pounding down onto my face, puddling in my eye sockets and running down into my ears. My face and hands were numb. My arms moved. I could breathe a little easier now.
Drenched in cold, relentless rain, Claire spies the spooky ghost of Otter-tooth. Careful, lest you get hyperthermic, Claire!

And, there he is. Sharp as an Otter’s Tooth!
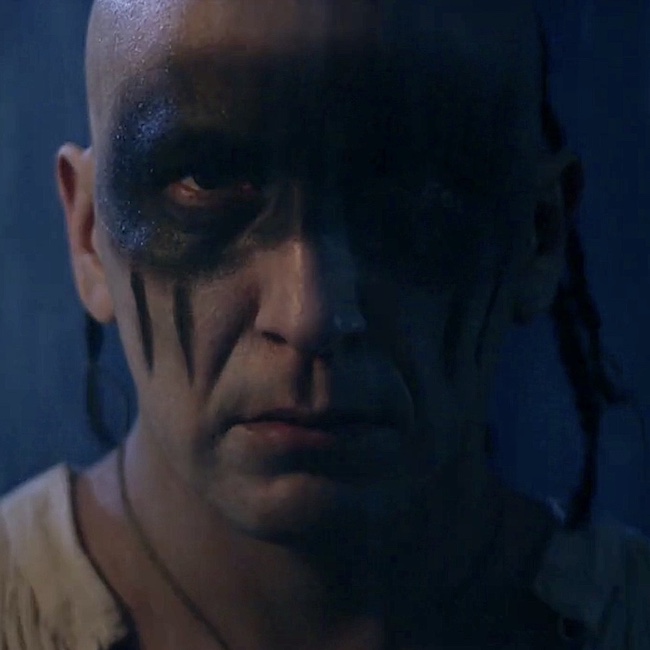

That is it for thermal injury. But….
Here’s some exciting thermal news: The US Department of Energy is developing clothes with thermal properties that adapt to the environment and to the wearer’s body. By changing the make-up or shuttling heat to and from the body, the garments can keep people comfortable whatever the external temperature (30 January 2016, New Scientist). I’m ready for one of these jackets, how about you?
Onward!
Alcohol: Alcohol is a colorless, volatile, and flammable liquid that is the intoxicating element of wine, beer, and other spirits (duh!); it is also used as a fuel and is an industrial solvent! 😮
How the body handles alcohol: The stomach lining contains alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), an enzyme which metabolizes alcohol. The liver also has ADH plus other enzymes that help break down alcohol. But, bad news for the lassies: Women naturally have lower levels of GAD than men and often develop higher blood alcohol levels after drinking the same or even less alcohol. So, be wary if ye are an XX!
Claire offers a pithy analysis of alcohol in this quote from the big book, “Drums of Autumn,“wherein Jamie gets John Quincy Myers drunk in preparation for his hernia surgery. (Psst…Non-book readers ken Claire performed this surgery on Edmond Fanning in episode 408, Wilmington.)
“Alcohol isn’t a good anesthetic at all,” I said, shaking my head. “It’s a poison. It depresses the central nervous system. Put the shock of operating on top of alcohol intoxication, and it could kill him, easily.”
And, there we have it in a nutshell!
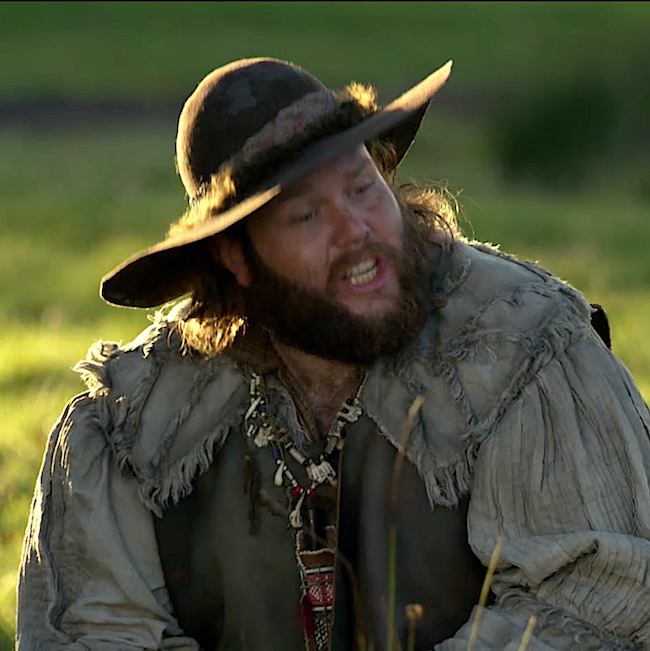

Not surprisingly, alcohol is the most widely used and abused toxic agent in the world. (Not meaning to preach as I enjoy a wee bit now and then)
Alcohol injury ranges from binge drinking to full on alcoholism with a myriad of accompanying ailments. Most of us are well-versed on the effects of excessive alcohol intake and realize some effects are acute and others are chronic.
Acute Alcohol Intoxication: In the US, there are over 3,000,000 reported cases of acute alcohol intoxication (AAI) from drinking too much, too quickly. Symptoms include slurred speech, incoordination, mood and behavioral changes, and poor judgement. Acute alcohol intake effects breathing, heart rate, body temperature, gag reflex, and can lead to coma and death. (psst… I wager many more cases go unreported) 🫢
Risk factors include:
-
-
- Injuries, such as motor vehicle crashes, falls, drownings, and burns.
- Violence, including homicide, suicide, sexual assault, and intimate partner violence.
- Alcohol poisoning, a medical emergency that results from high blood alcohol levels.
- Risky sexual behaviors, including unprotected sex or sex with multiple partners. These behaviors can result in unintended pregnancy or sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV.
- Miscarriage and stillbirth or fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) among pregnant women.
-
Oh, Jamie is in the throes of AAI at Lallybroch (episode 112, Lallybroch). He is stinking drunk as he stumbles into the bedchamber reeking of booze; Claire is not “amoozed.”
But, he looks marvelous in his da’s splendid leather coat! 😜

-
- High blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, liver disease, and digestive problems.
- Cancer of the breast, mouth, throat, esophagus, larynx, liver, colon, and rectum.
- Weakening of the immune system, increasing the chances of illness.
- Learning and memory problems, including dementia and poor school performance.
- Mental health problems, including anxiety and depression.
- Social problems, including family problems, job-related problems, and unemployment.
- Alcohol use disorders, or alcohol dependence
In season six of Outlander, we witness Fergus falling into ADS as he struggles with the cruelty and intolerance toward his dwarf son (episode 603, Temperance). Alcohol is commonly used to cope with personal tragedy and trauma.
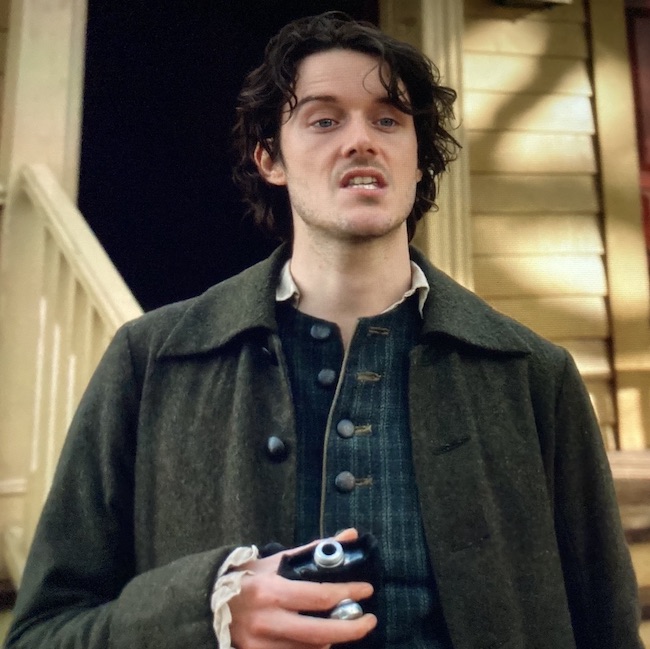

You remember Colum MacKenzie back in Outlander, seasons 1 and 2? Yes, of course ye do! 😊 Claire diagnosed Colum as a sufferer of Toulouse-Lautrec Syndrome, also known as pycnodysostosis.
Colum required large quantities of rhenish wine (9% alcohol content) to quell and dispel the agony of his existence (Outlander episode 102, Castle Leoch).
… “I beg your pardon?” I turned, having missed Colum’s words in the growing noise, to find him offering me the decanter, a lovely bell-shaped thing of pale green crystal.
The liquid within, seen through the glass, seemed green as the sea-depths, but once poured out it proved to be a beautiful pale-rose color, with the most delicious bouquet. The taste was fully up to the promise, and I closed my eyes in bliss, letting the wine fumes tickle the back of my palate before reluctantly allowing each sip of nectar to trickle down my throat.
“Good, isn’t it?” The deep voice held a note of amusement, and I opened my eyes to find Colum smiling at me in approval. I opened my mouth to reply, and found that the smooth delicacy of the taste was deceptive; the wine was strong enough to cause a mild paralysis of the vocal cords.
“Won—wonderful,” I managed to get out. Colum nodded.
“Aye, that it is. Rhenish, ye know. …”
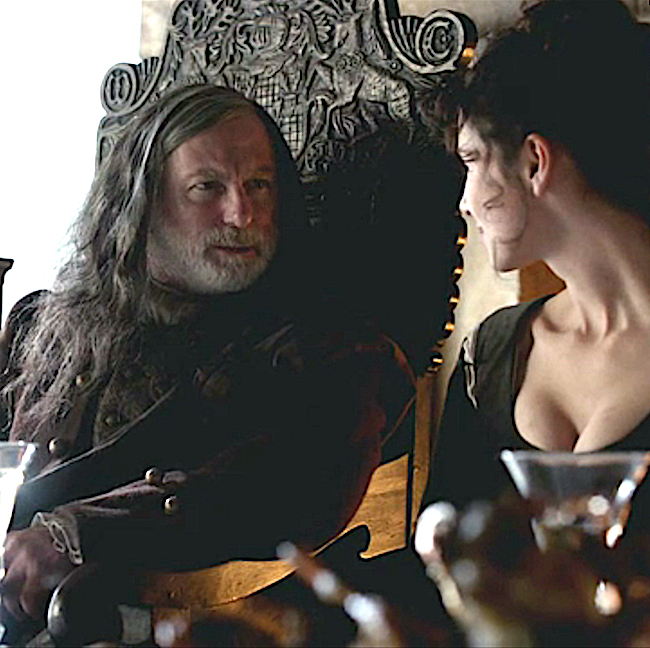

Clearly, Colum suffered from his genetic disability but also from ADS . Near the end, when rhenish no long offered the needed relief, he turned to Claire to assist him in end of life options (Outlander episode 210 Prestonpans).
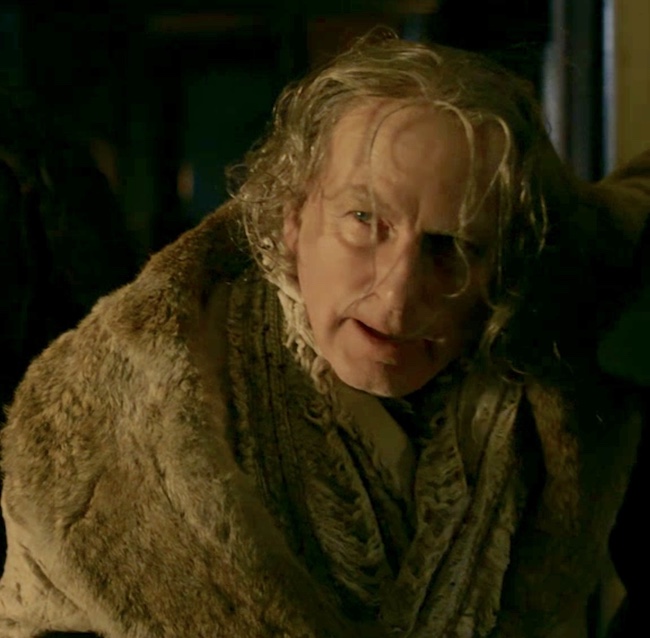

ADS is considered a medical emergency because it can lead to coma and death. Guidelines exist about the amount of alcohol the liver can metabolize per hour and these rates should not be exceeded. Again, please get informed if this is an issue in your life.
As a final example, we see wee Flora MacDonald taking a wee nip from her personal hip flask in Outlander, episode 605, Give Me Liberty! Now, just because she carries a personal flask, it doesn’t mean she is suffering from either acute or chronic alcohol poisoning! 😉
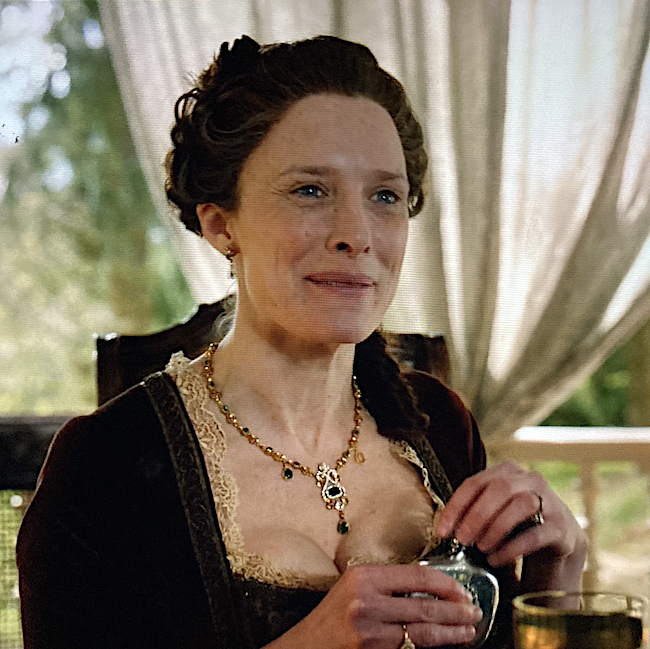

Finally, this is an interesting tidbit. Some people carry a gene variant encoded for alcohol dehydrogenase (ALDH2*2) that stops the enzyme working, so these folks experience flushing soon after drinking. This happens because they have a lowered ability to metabolize alcohol and includes some 8% of the world’s population. Now, a link has been found showing that this gene raises heart disease risk in those who experience alcohol flush (New Scientist, 4 Feb. 2023). The risk of heart disease is four times greater in regular drinkers with the defective gene! if you flush immediately after alcohol ingestion, you may wish to consult your physician?
OK, that is our lesson for today. But before we call it quits let’s have a –
Pop Quiz!
Name the injury (red arrow) Jamie sports after the Battle of Alamance, in Outlander episode 507, The Ballad of Roger Mac.
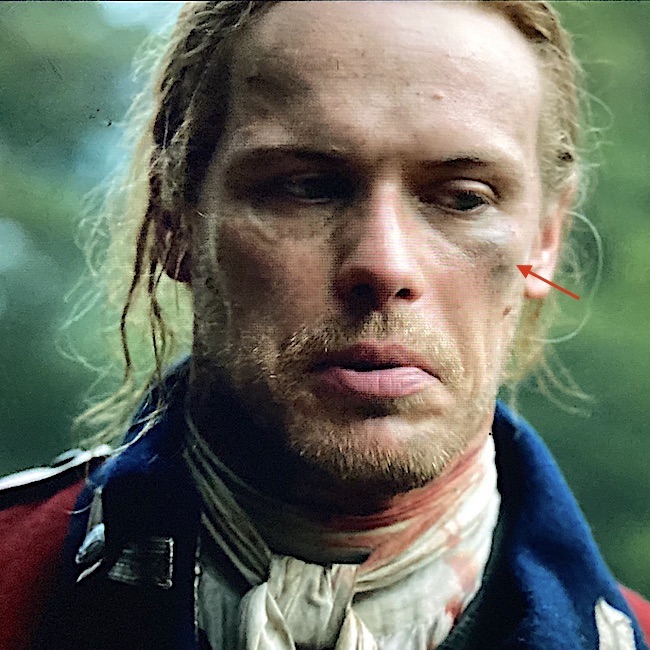

What was that you said?
An abrasion? 🚫
A laceration? 🚫🚫
An avulsion? 🚫🚫🚫
What was that you said?
A contusion? Yep!
Well done, anatomy students! 👏🏻👏🏻👏🏻
Next time, Part 3!
The deeply grateful,
Outlander Anatomist
Follow me on:
-
- Twitter: @OutLandAnatomy
- Facebook: OutlandishAnatomyLessons
- Instagram: @outlanderanatomy
- Tumblr: @outlanderanatomy
- Youtube: Outlander Anatomy
Photo creds: Sony/Starz, www.en.wikipedia, www.britannica.com
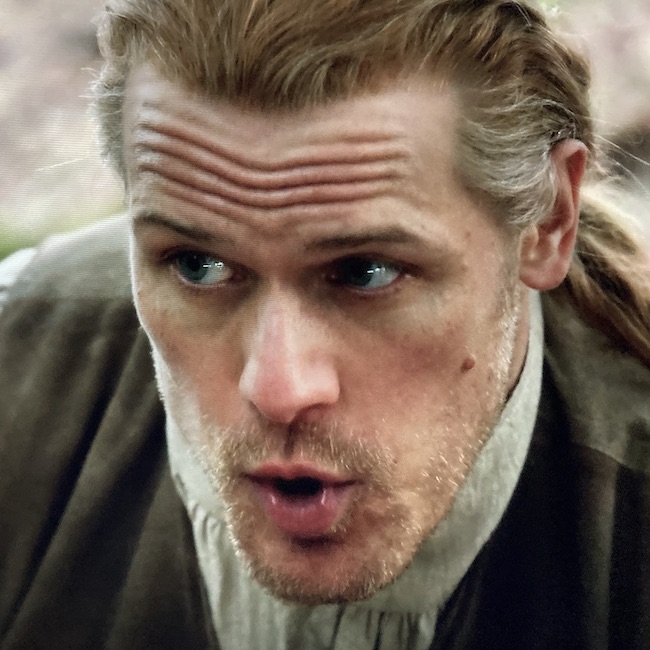


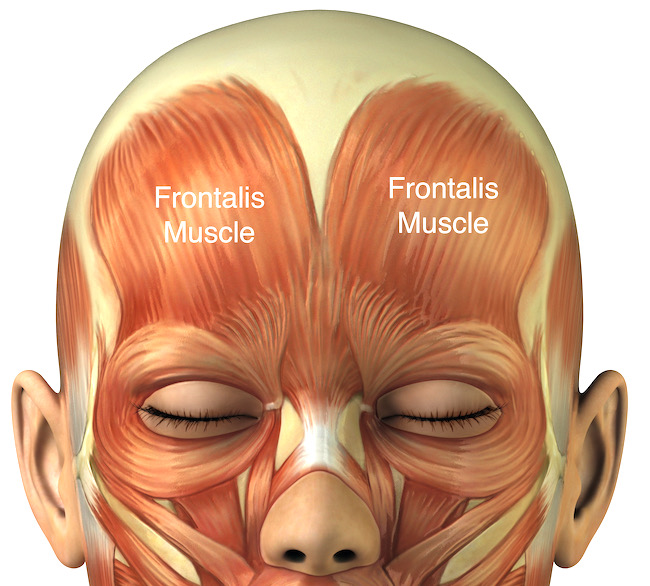
 Anatomy def: Frontalis muscles lift the eyebrows and wrinkle the forehead
Anatomy def: Frontalis muscles lift the eyebrows and wrinkle the forehead