 Anatomy Def: To inflame is the body’s response to injury.
Anatomy Def: To inflame is the body’s response to injury.
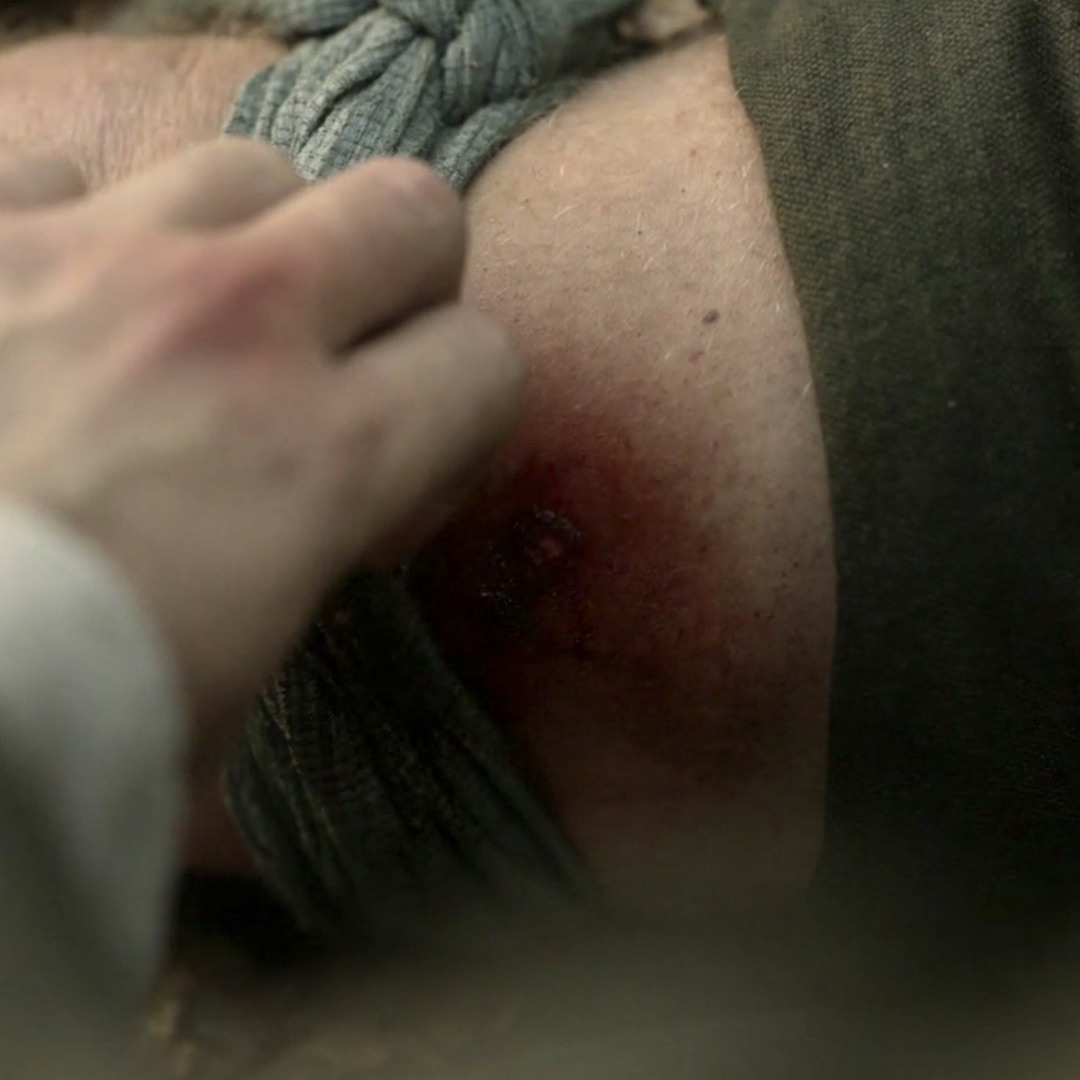
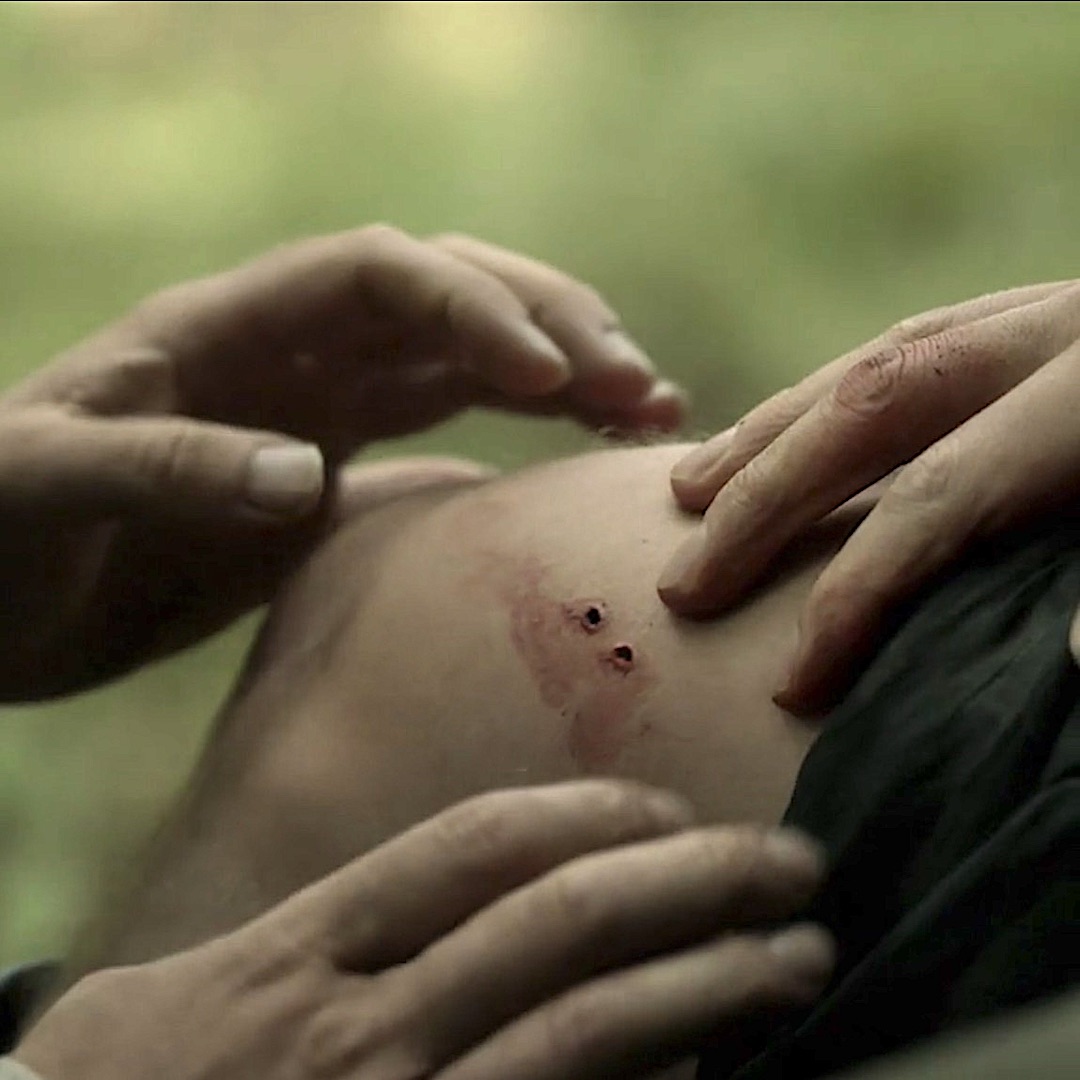
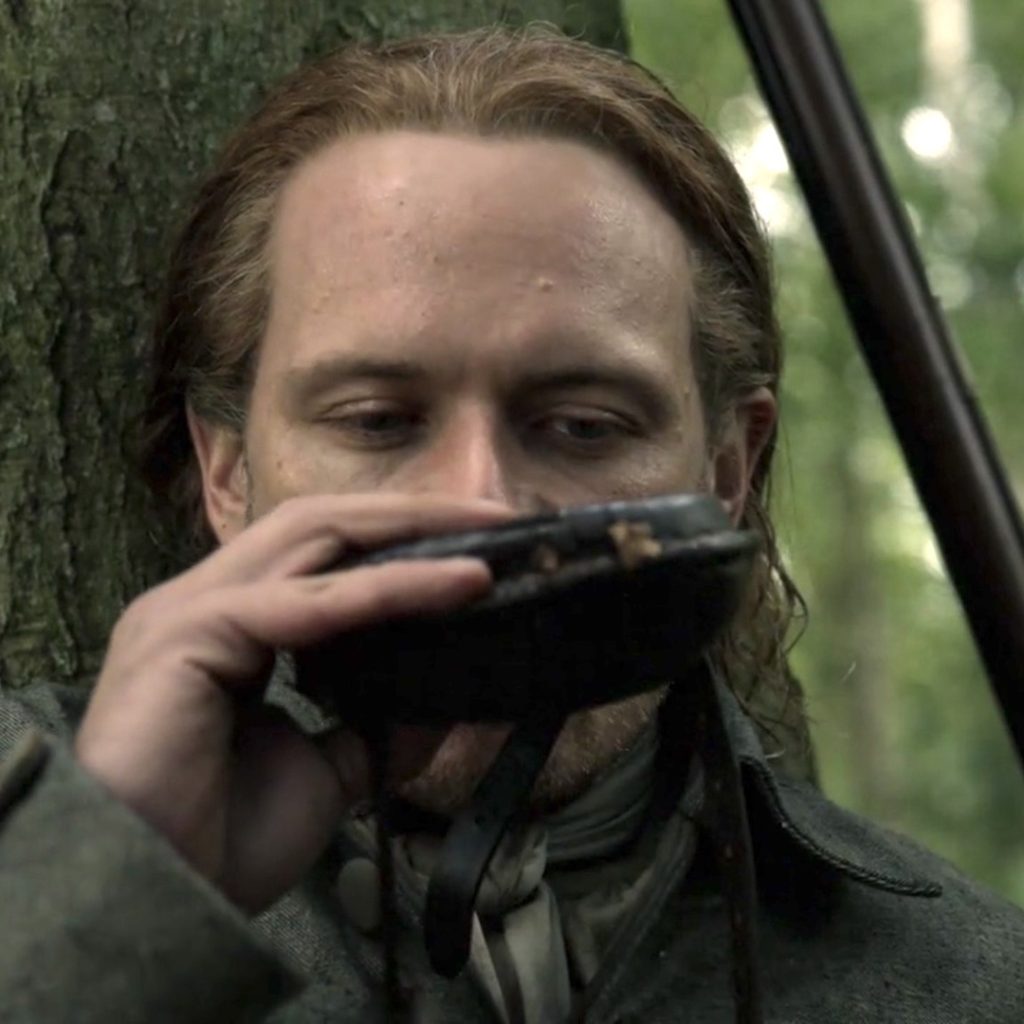
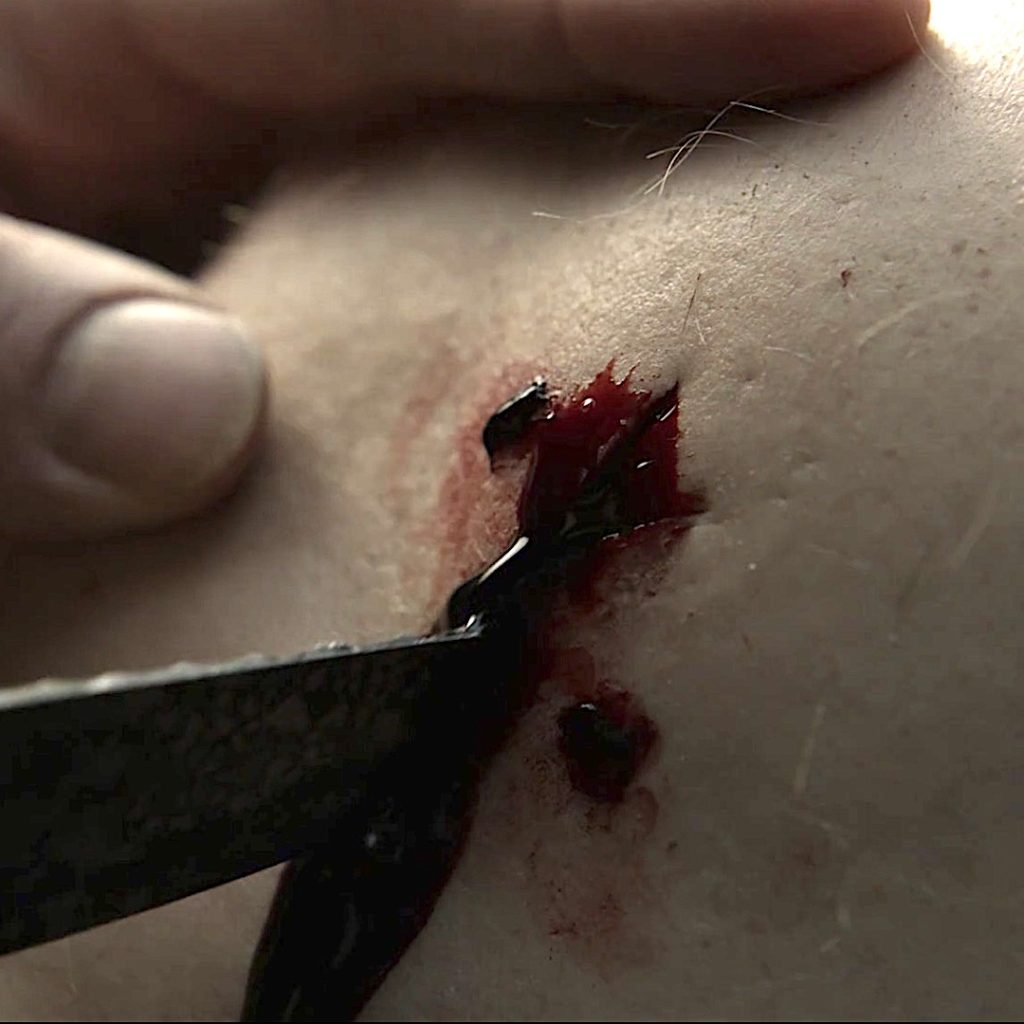
Outlander Def: Ow! Jamie’s puir, inflamed leg after the horrid fang-bang! 🐍
Learn about inflammation in Anatomy Lesson #37, “Outlander Owies – Mars and Scars.” Just to be clear, inflammation is the process of being inflamed.
Inflammation is an crucial defense mechanism the body employs to combat physical injury. There are two main types:
-
- Acute – rapid but short-lived response to injury
- chronic – prolonged response to injury (different types)
Just so you know, acute inflammation is not the same as infection, although these may occur simultaneously.
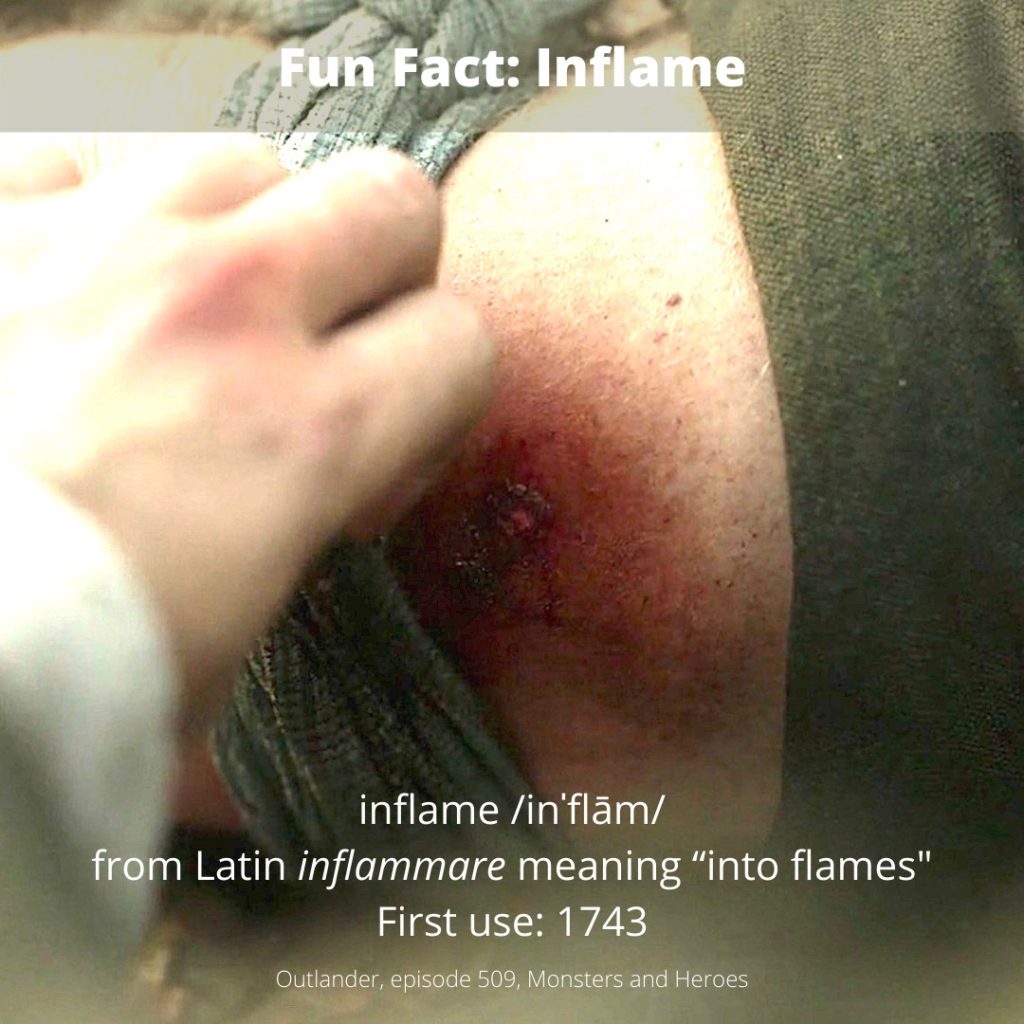
Fact: Nearly 2,000 years ago, the Roman, Aulus Cornelius Celsus, wrote prolifically about medicine, pharmacy, surgery, agriculture, law and military arts! 😲 Celsus was not a physician, but he was the first to described the four cardinal signs of acute inflammation. Later, in the 19th century, Rudolf Virchow, the father of modern pathology, added a fifth.
The five signs, in Latin, followed by their English equivalents, are:
-
- Rubor = redness
- Tumor = swelling
- Calor = heat
- Dolor = pain
- Functio laesa = loss of function (Virchow)
How does inflammation happen? It is a process rather than an event. Simply put, if tissues sustain an injury, inflammation quickly appears due to dramatic changes in small blood vessels of the injured region. Blood flow increases. Small vessels become leaky allowing fluid (plasma) and some white blood cells (WBC) to enter the injured tissues. So:
-
- Increased blood flow causes redness
- Leaked plasma causes swelling
- Leaked WBCs release chemicals that induce more redness, swelling, pain, and increased temperature (heat)
- Finally, pain causes decreased function of the injured area (Ouch! Using it hurts!)
Inflammation may seem harmful, and sometimes it is, but it is designed to:
-
- Eliminate the cause of tissue injury
- Remove damaged cells
- Pave the way for tissue repair
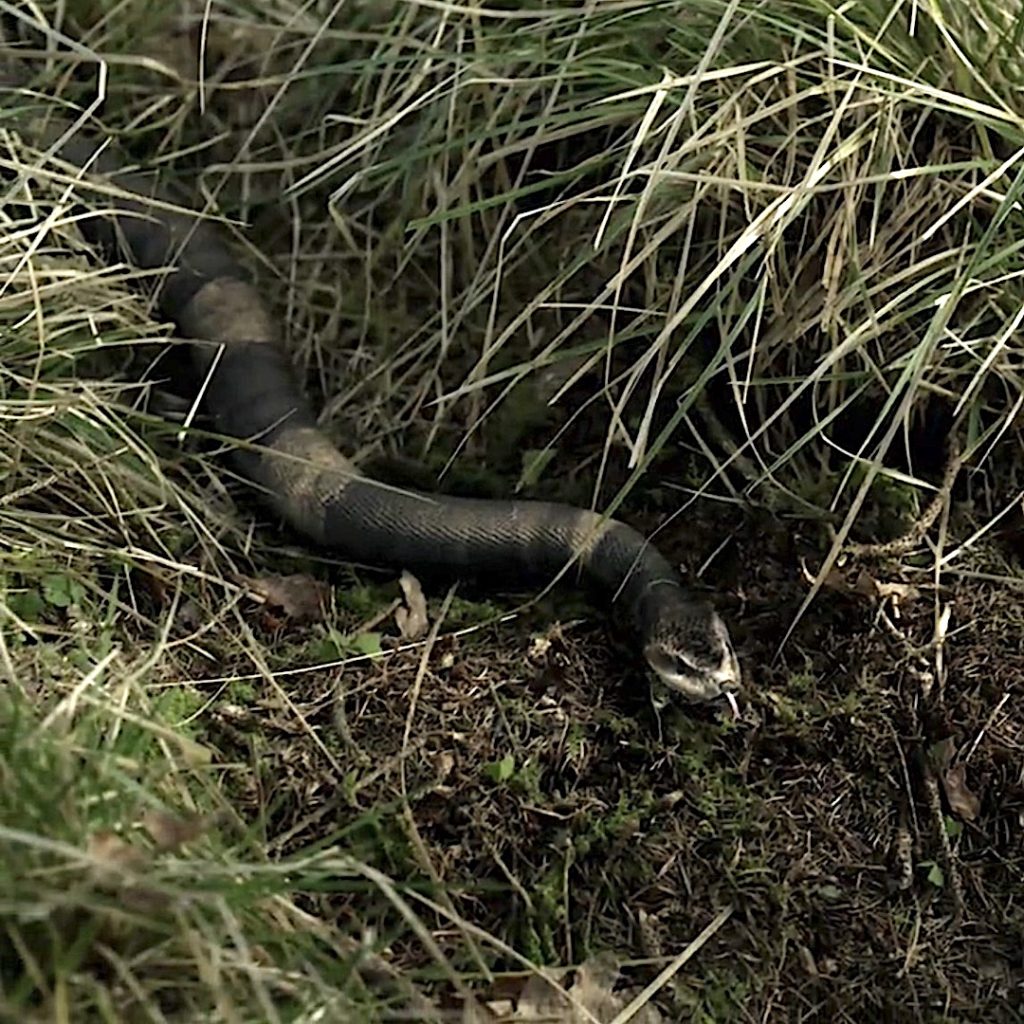
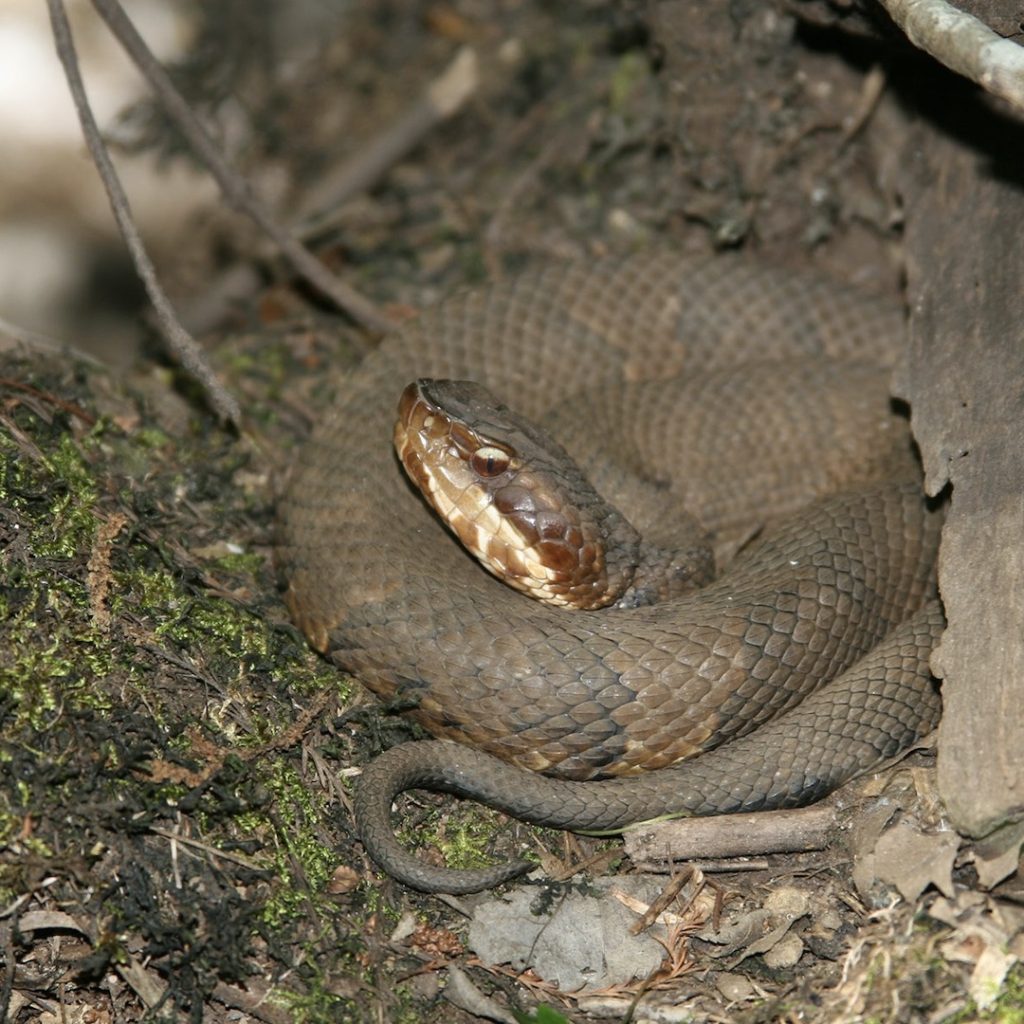
Just to be complete, a venomous snake bite usually produces (there can be other symptoms depending on venom):
-
- Severe burning pain at the site
- Swelling
- Redness and bruising all the way up arm or leg
- Nausea
- Labored breathing
- Weakness
- Odd taste in mouth
Try This: The next time you get cut or scratched, look carefully at the wound for redness and swelling. Is it painful? Gently place the wounded area against the lip to detect an increase in temperature. Yup, there are the four signs. And, if you are like most folks, you will avoid using that area until it heals, hence, loss of function!
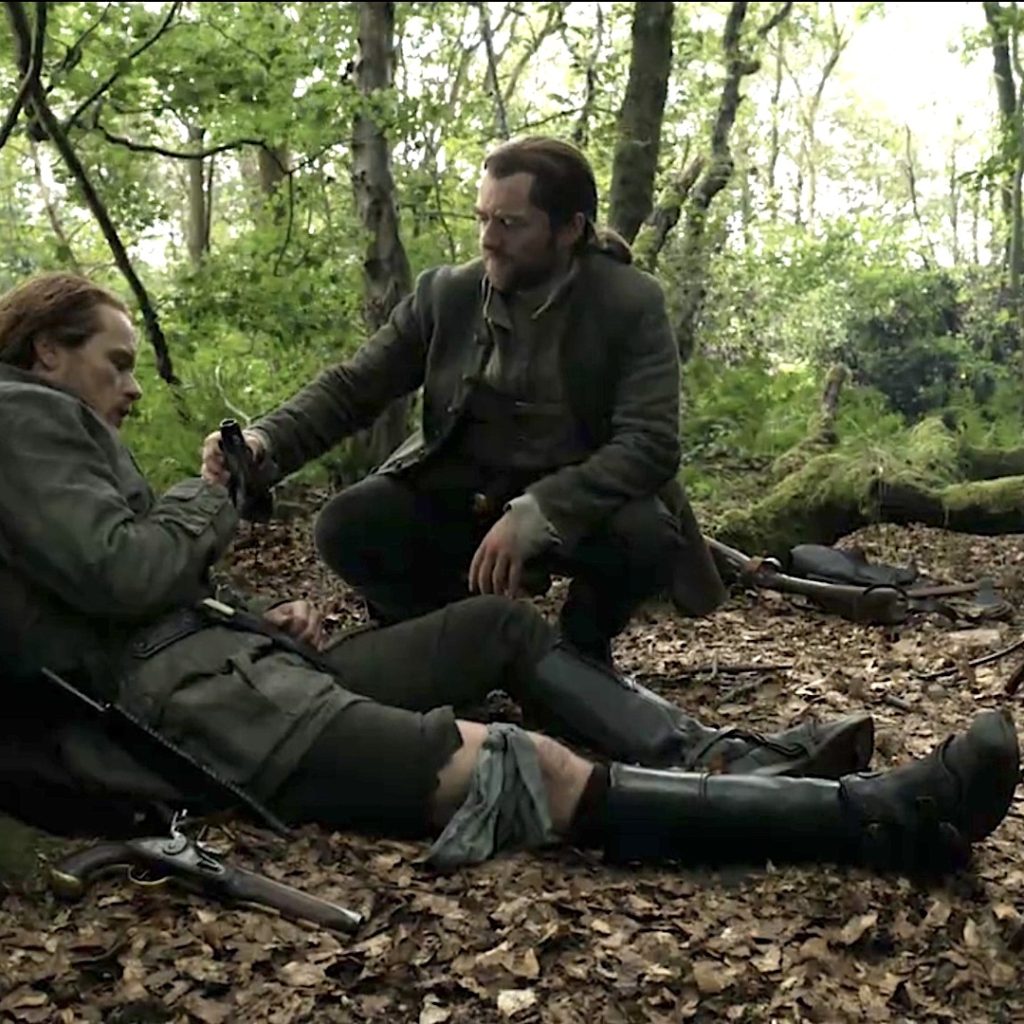
Read about Jamie’s inflamed leg in The Fiery Cross! Yes, it’s in there!
“That’s enough, aye?” Jamie said mildly. “You’ll drain me dry.” He gingerly wiggled his bared foot, grimacing at his leg. The slashmarks were vivid, still oozing blood, and the flesh around them was swollen from the sucking, blotched and bruised.
The leg was noticeably swollen near the bite, and the blue tinge had spread; it showed like a faint fresh bruise on either side of the encircling handkerchief.
See Jamie’s inflamed thigh in Outlander episode 509, Monsters and Heroes! Och, this is only the start of his thigh-high response to that vicious fang-bang! Monster, indeed!!! 😳
The deeply grateful,
Outlander Anatomist
Follow me on:
-
- Twitter @OutLandAnatomy
- Join my Facebook Group: OutlandishAnatomyLessons
- Instagram: @outlanderanatomy
- Tumblr: @outlanderanatomy
- Youtube: Outlander Anatomy
Photo Credits: Sony/Starz