Greetings Outlander anatomy students!
I have not posted a lesson or fun fact since September of last year! Time to get back into the dissection room. 🤓
I plan to post several lessons in succession, all dealing with trauma-drama on Outlander! And, as we all ken, there is plenty of this to go around.
Let’s get started with a couple of definitions.
As many of you know, the term anatomy comes from the Greek ana– (up) + temnein (to cut). Taken literally, anatomy means to cut away or to reveal.
Today’s Anatomy Lesson will reveal topics belonging to the science of pathology: Greek meaning pathos (suffering) + ology (to know). Interestingly, pathology is literally the study of abnormal anatomy so we are well within our lane!
Although this topic is not light-hearted, it is an important one which may prove useful to you and yours.
Pathologists have meticulously developed a logical, useful, and understandable schema to classify the types of trauma which injure body cells, tissue, and organs. Major categories are mechanical trauma, thermal injury, alcohol, infectious agents, and so on.
Today lesson will focus only on mechanical trauma, of which there are seven types:
-
- Contusion
- Abrasion
- Laceration
- Incision
- Avulsion
- Projectile injury
- Puncture wound
Whew, that is quite a laundry list! Call it a miracle that any of us survive to adulthood. 🙏🏻
Diana’s Outlander books plus the Starz Outlander series are rife with excellent examples of varied and sundry mechanical trauma-drama so it is time for Jamie.com to hop atop the dissection table. Up you go!
As we explore Mechanical trauma, bear in mind this type of injury produces two types wounds:
-
- closed wounds – the skin is intact
- open wounds – skin is scraped, torn, cut, or punctured
You will see these terms appear in the lesson.
Almost every Outlander episode contains one or more of the seven types of mechanical trauma, so let’s go find some!
Contusion: The contusion is closed trauma so the skin remains intact. Caused by blunt force, blood vessels are ruptured and blood seeps into surrounding tissues forming a hematoma (Greek, meaning blood tumor).
Known as a bruise in laymen’s terms, the appearance of a contusion is due to extravasated blood in the tissues. Press on a skin contusion and it does not blanch under pressure. Interestingly, hematomata (pl.) also occur in internal organs such as brain and liver.
Claire provides a heart wrenching example of contusion after she is kicked and bludgeoned by Lionel Brown and his band of hairy men! In the final scene of Outlander episode 512, Never My Love, her contusions caused by blunt force trauma are on full display!
Chapter 28 of Diana’s sixth big book, A Breath of Snow and Ashes, describes the carnage in shocking detail; the blows were administered by thief-taker, Harley Boble:
“He was standing. He was kicking me and cursing, panting and half-sobbing as his boot thudded into sides and back and thighs and buttocks. I panted in short gasps, trying to breathe. My body jerked and quivered with each blow, skidding on the leaf-strewn ground, and I clung to the sense of the ground below me, trying so hard to sink down, be swallowed by the earth.”
The uneven mottling of Claire’s skin created by the FX crew is accurate. A rainbow of blue, black, green, and yellow herald the normal healing pattern of contusions, although it takes a wee bit of time for the full range of colors to appear.
Puir Claire! Her emotional trauma will linger far after her physical wounds have healed. 😔
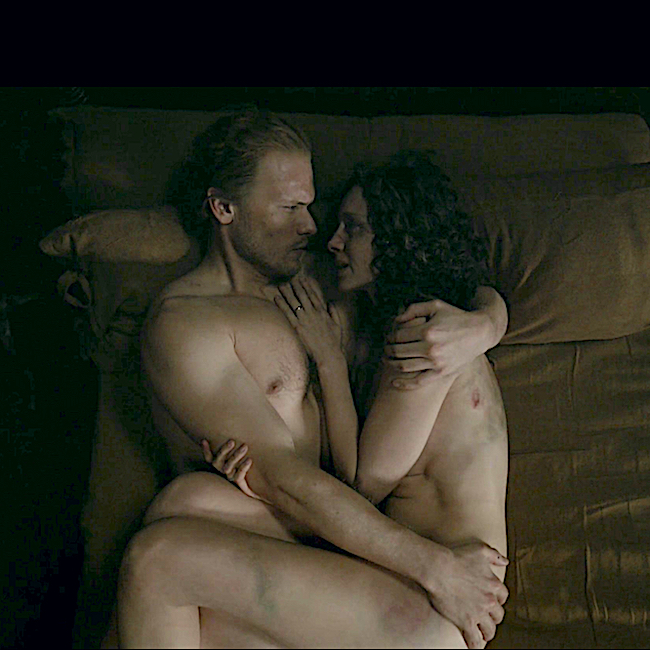

Abrasion: The abrasion is an open type of mechanical injury wherein the epidermis (Anatomy Lesson #5) is rubbed or scraped away. Superficial abrasions typically turn red whereas deep abrasions ooze blood making them easily distinguishable. The good news is the skin repairs abrasions rather promptly and without scarring unless infection messes with the healing process.
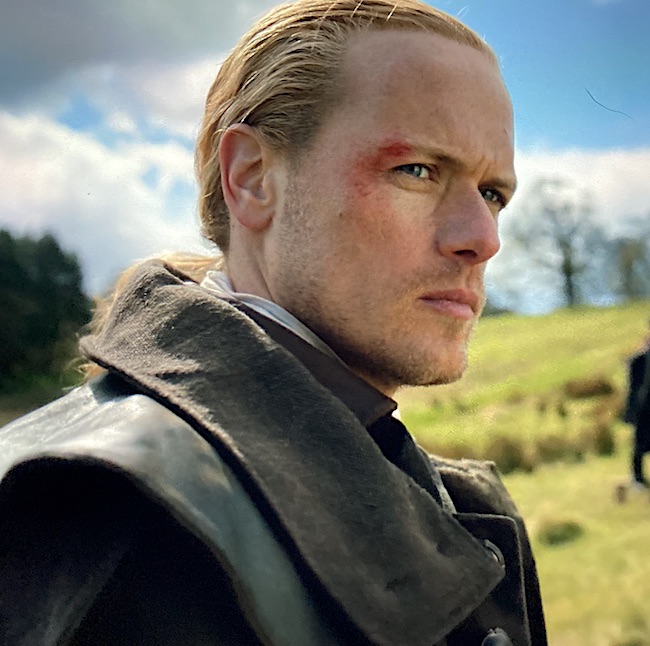
Jamie is our victim for the abrasion! Here in Outlander episode 608, I Am Not Alone, we see a mostly superficial abrasion of his right brow and cheek as a result of the Richard Brown and his men attempting to take Claire into custody for the murder of Lionel. His skin is scraped and bright red. Again, kudos to the special effects and detail folks.

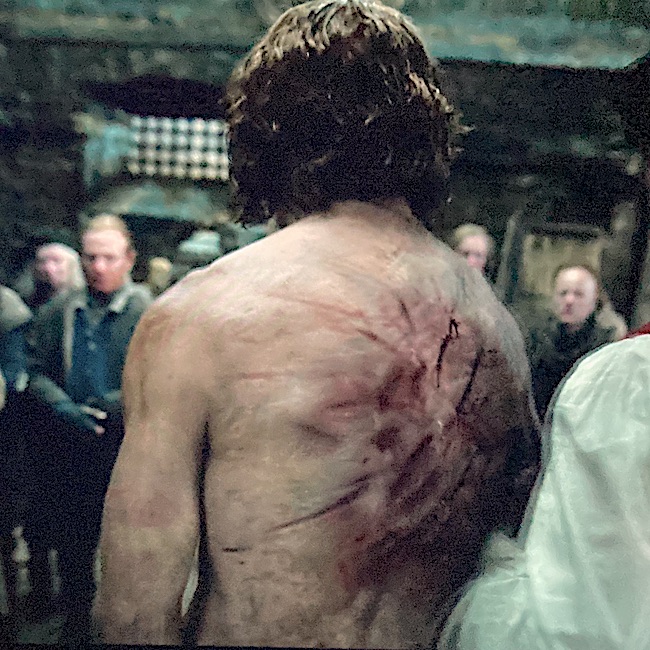
Laceration: Our next trauma is a laceration, best defined as a slash or tear. Lacerations are open wounds with rough and ragged margins that may be contaminated with bacteria and debris. Most often, they are tears of the skin, but internal organs can also be lacerated.
In a flashback during Outlander episode 601 Echoes, Jamie relives his years at Ardsmuir as Mac Dubh wherein he takes responsibility for an illegal piece of tartan and receives lashes on his already scarred back. Trauma-drama for sure!
The scene is poignantly described in Diana’s third big book, Voyager:
He had nodded to the two privates, who seized the prisoner’s unresisting hands and raised them, binding them to the arms of the whipping post. They gagged him, and Fraser stood upright, the rain running down his raised arms, and down the deep seam of his backbone, to soak the thin cloth of his breeches.
“ … in contravention of the Diskilting Act, passed by His Majesty’s Parliament, for which crime the sentence of sixty lashes shall be inflicted.”
“…Mr. Fraser, you will take your punishment.”
“…The sergeant-farrier paused only briefly between blows. He was hurrying it slightly; everyone wanted to get it over and get out of the rain. Grissom counted each stroke in a loud voice, noting it on his sheet as he did so. The farrier checked the lash, running the strands with their hard-waxed knots between his fingers to free them of blood and bits of flesh, then raised the cat once more, swung it slowly twice round his head, and struck again. “Thirty!” said the sergeant.
Puir Jamie. His back is broad and strong, but gah! 😵💫

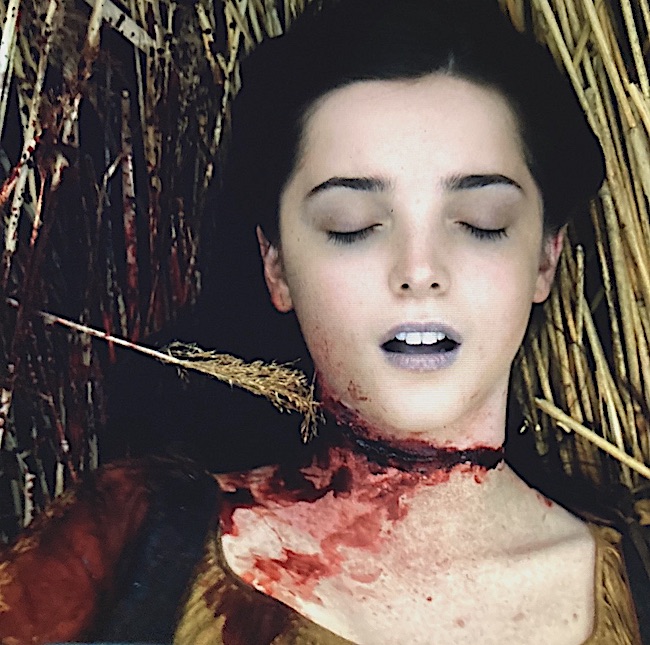
Incision: An incision is an open wound that differs from the laceration because it is made by sharp cutting instruments such as knife, razor, or glass edge. Thus, the margins of an incision are sharp and well-defined.
Today, incisions are closed with different suturing techniques depending on the site and type of wound. There are also different types of suture materials including thread, needles, stitches, and knots as well as closures without sutures such as staples and glue. The clean margins permit incision wounds to be closed tidily and these typically heal with minimal scarring.
Unfortunately, there was no suturing of Malva’s mortal wound although it is a perfect example of incision injury (Outlander episode 606, The World Turned Upside Down).
This poignant scene is captured, again from Diana’s sixth big book, A Breath of Snow and Ashes:
I smelled the blood and saw her in the same instant. She was lying in the salad bed, her skirt flown out like some gigantic, rusty flower blooming amid the young lettuces.
I was kneeling by her, with no memory of reaching her, and the flesh of her arm was warm when I grasped her wrist—such small, fragile bones—but slack, there was no pulse—Of course not, said the cold small watcher inside, her throat is cut, there’s blood everywhere, but you can see the artery isn’t pumping; she’s dead.
Malva was a damaged young woman who, in turn, damaged others. Even so, she scarcely deserved to die in such a despicable manner. 😯 Puir lass.
Who did the dastardly deed? We will soon find out when Season seven airs!
(Pssst….Another excellent example of incision trauma would be Claire’s surgical repair of Tom Christie’s Dupuytren contracture. Yes, I did write a lesson on this topic.)

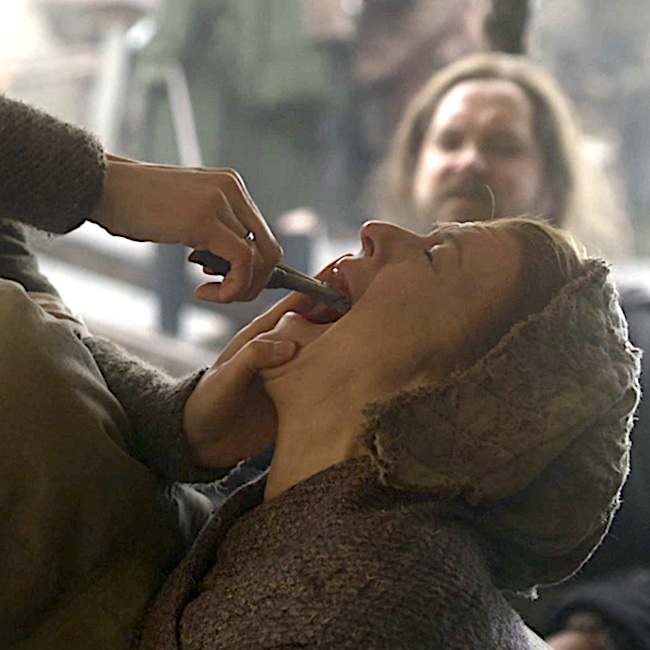
Avulsion: An avulsion injury is the forcible tearing away of a body part or structure. This type of trauma was the hardest to find in Outlander. I had to go all the way back to Season two! But, find one, I did: a good example of avulsion is the tooth extraction Claire performed in Outlander episode 211, Vengeance is Mine!
Although avulsion more commonly describes a muscle pulled from its bony attachment or limbs (e.g. finger, toe) being torn off, a tooth being separated from its socket surely qualifies. Ouch! 🫣
Is Rupert is amused or scared s**tless? We miss you, man!

Projectile Injury: Projectiles are objects that are propelled forward by an external force. Thus, a hurled stone is a type of projectile. Projectiles typically cause open wounds and probably the best-known is the gunshot wound (gsw).
The degree of tissue disruption caused by a projectile is proportional to its kinetic energy, yaw (twist), fragmentation of the projectile; all features that especially apply to a gsw.
I certainly am not a munitions expert but as I understand it, today’s standard NATO weapon (M16 rifle) fires a cartridge that measures .21” (5.56mm) in diameter. But an 18th century musket ball ranged from .51”-.75” (13-19mm) in diameter making it two to three times the diameter of the M16 cartridge – one humongous projectile!!!
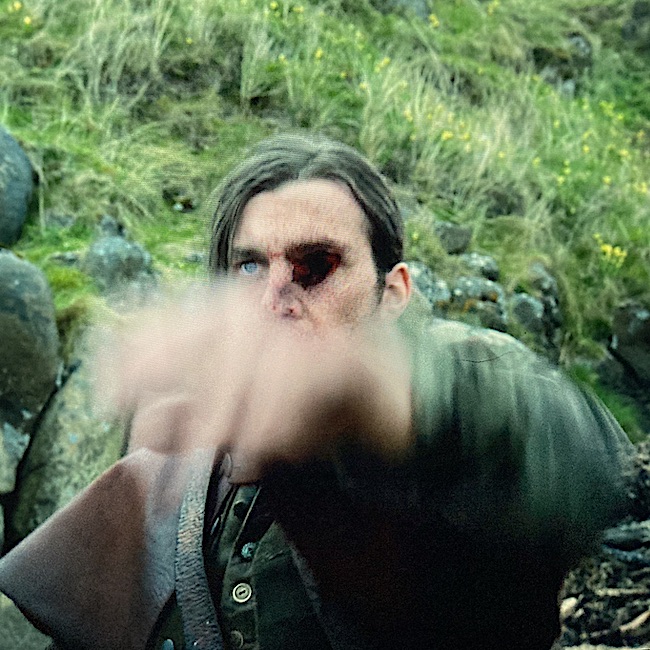
Season six ended with a startling but effective example of a projectile (Outlander episode 608, I Am Not Alone).
Several of Brown’s men kidnapped Jamie, planning to put him aboard a ship bound for far off places. Chief Bird came to the rescue, shooting the abductor with a rifle given to him by Jamie. Bullseye (so to speak)! 😉
Chief Bird nods in satisfaction at Jamie:
“I told you I would fight with you, Bear-Killer.”
Until about 1880, the standard practice for treating gsw required that physicians probe and locate the path of a projectile with unsterilized fingers. Before this time, germ theory and Lister’s dilute carbolic acid treatment for “antisepsis surgery” were unknown.
Understand, the musket ball is not only large, it is a low velocity projectile, so its sheer mass literally plows (yikes!) a path through tissues. Little wonder that it leaves a gaping hole! In fact, in those by-gone days, one musket ball was sufficient to kill a man if it struck near any vital organ. And, if the victim survived a musket ball wound, he/she often succumbed to the effects of a subsequent amputation or infection.
I might add, that the impact of the musket ball would have knocked this kidnapper on his ass. But, for a second he remains upright for dramatic effect! 😮

Puncture Wounds: Puncture wounds are open wounds that pierce the skin and penetrate underlying tissues. These are difficult to cleanse and thus increase the risk of infection.
Further, if the puncturing object stays in the body, then it is a penetrating wound; if it passes through the body and emerges then it becomes a perforating wound.
Understand that it is not uncommon for wound classifications to overlap so, for instance, a gsw might be categorized as both a projectile and a penetrating or a perforating wound.
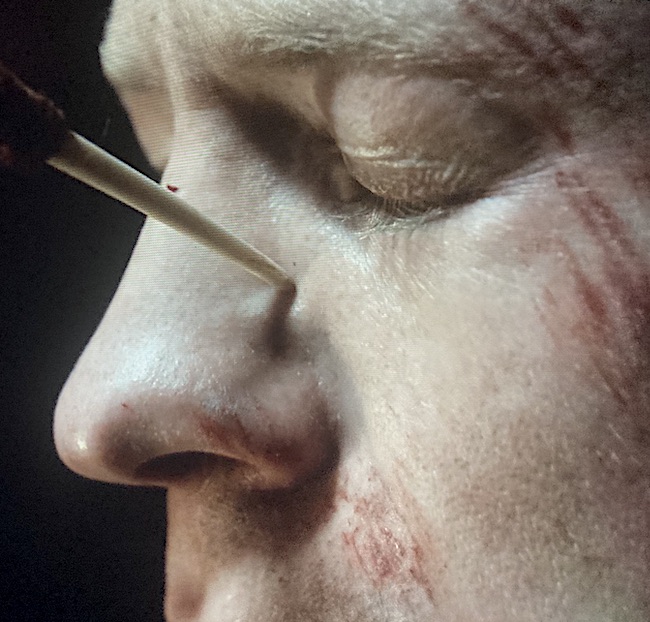
A great example of a puncture wound occurs during Ian’s voluntary adoption into the Mohawk tribe in the form of ritualistic tattooing. This was done with what appears to be a porcupine quill in Outlander episode 604, Hour of the Wolf. Ouch!
This is the description of Ian’s transformation from Diana’s fourth big book, Drums of Autumn:
“Ian? Is that you?”
“Aye, Uncle. It’s me.”
His voice sounded odd; breathless and uncertain. He stepped into the light from the smokehole and I gasped, feeling as though I had been punched in the stomach.
The hair had been plucked from the sides of his skull; what was left stood up in a thick crest from his scalp, a long tail hanging down his back. One ear had been freshly pierced and sported a silver earring.
His face had been tattooed. Double crescent lines of small dark spots, most still scabbed with dried blood, ran across each cheekbone, to meet at the bridge of his nose.
Also, notice the abrasions on his left upper lip, nostril, cheek, brow and temple? His dash through the gauntlet took its toll, for sure! 😱

Whew! We covered all seven types of trauma drama, probably enough for one lesson!
Final Thought: Here’s an important take-home message I learned from my surgical colleagues: if you encounter a projectile wound in which the penetrating object is still in the body, do not attempt to remove it in the field! Instead, transport the victim to the nearest emergency room ASAP so professionals can remove it under medically-controlled conditions.
Tempted to remove a projectile yourself? Don’t! (Well, maybe a sliver is OK.) Seriously, this advice is because the embedded object usually exerts pressure on nearby torn blood vessels squelching blood loss. After the object is removed, the resultant blood flow may not be easily staunched especially if a vital organ is involved.
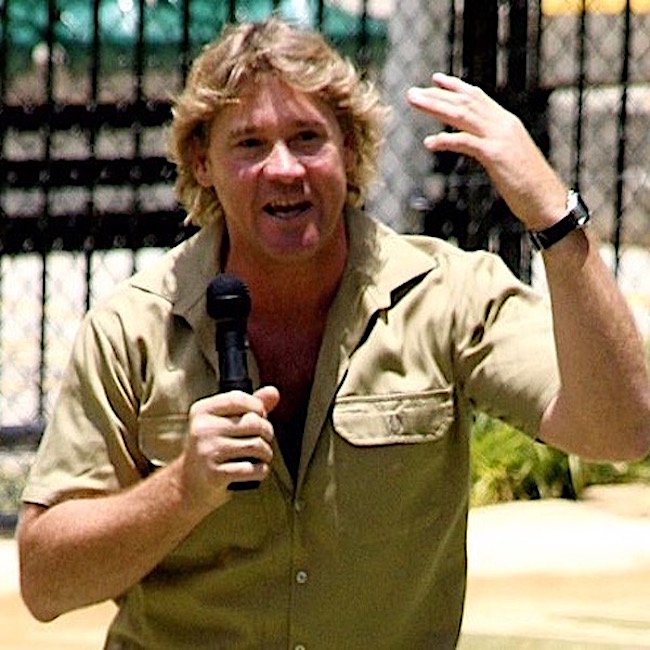
This happened to the late, great Steve Irwin, Crocodile Hunter, who removed a stingray barb that penetrated his heart. Sadly, he bled to death in moments through the hole in his chest!

Stay tuned for a future lesson on trauma drama!
The deeply grateful,
Outlander Anatomist
Follow me on:
-
- Twitter @OutLandAnatomy
- Join my Facebook Group: OutlandishAnatomyLessons
- Instagram: @outlanderanatomy
- Tumblr: @outlanderanatomy
- Youtube: Outlander Anatomy
Photo credits: Sony/Starz, www.en.wikipedia